Gordon-Taylor Equation
Several approaches have been proposed for estimating the glass transition temperature of mixtures and random copolymers from knowledge of the properties of the pure components. Although different in detail, the proposed relationships are all based on the additivity of basic thermophysical properties. One of the most popular equations for predicting glass transition temperatures of amorphous mixtures and random copolymers is the Gordon-Taylor equation:(1)
Tg,mix ≈ [ω1 · Tg,1 + K · ω2 · Tg,2] / [ω1 + K · ω2 ]
where Tg,mix and Tg,i are the glass transition temperature of the mixture and of the components, ωi is the mass fraction of component i and K is an adjustable fitting parameter. If no experimental data are available, the constant K can be set equal to the change of the heat capacity when crossing from the glass to the rubber state, ΔCpi. For mixtures with two or more components this equation is given as
Tg,mix ≈ ∑i [ωi · ΔCpi Tg,i] / ∑i [ωi · ΔCpi ]
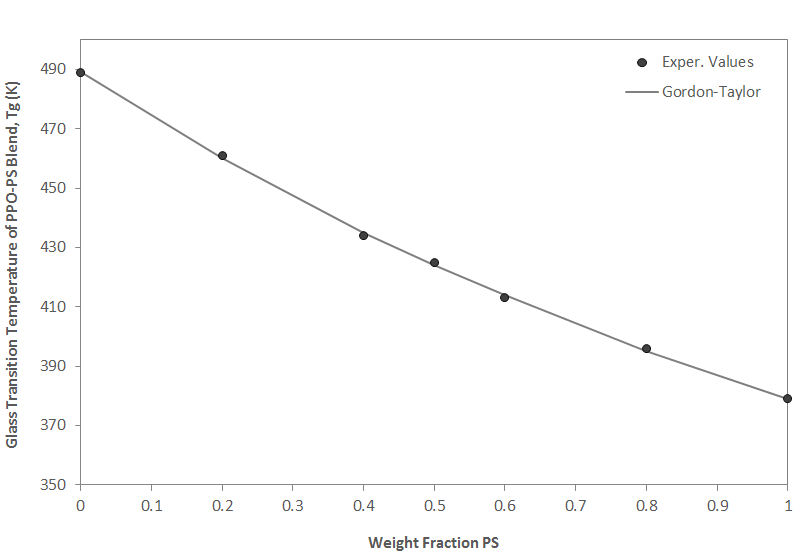
The Gordon-Taylor equation has been shown to be successful for fitting the glass transition temperature of many random copolymers. It can also be used to describe the composition dependence of miscible polymer blends exhibiting negative and positive deviation if K is treated as an adjustable parameter. However, the Gordon-Taylor equation should only be applied to blends and mixtures with relative weak specific intermolecular interactions. Otherwise, large deviations from the true Tg of the mixture can be expected. A suitable example would be a blend of polystyrene (PS) and poly(2,6-dimethyl-p-phenylene oxide) (PPO). Both polymers have similar structural groups and no specific interactions are present. The predicted values for such a blend (see below) are in good agreement with the experimental values (2)
.| Weight Fraction PS | Exper. Tg (K) | Predicted Tga (K) | Predicted Tgb (K) |
| 0 | 489 | 489 | 489 |
| 0.2 | 461 | 460 | 459 |
| 0.4 | 434 | 435 | 434 |
| 0.5 | 425 | 424 | 423 |
| 0.6 | 413 | 414 | 413 |
| 0.8 | 396 | 395 | 395 |
| 1.0 | 379 | 379 | 379 |
Glass Transition Temperature of PS-PPO blends
Glass Transition Temperature of PS-PPO blends
References
- M. Gordon, J. S. Taylor, J. Appl. Chem. 2, 495 (1952)
- L. An, D. He, J. Jing et al., Eur. Polym. J., Vol. 33, No 9, 1523 - 1528 (1997)