Polyxylylene Adipamide (PA-MXD6)
Properties and Applications
Polyxylylene adipamide, often abbreviated as PA-MXD6, PMXD6 or Nylon-MXD6, is a thermoplastic crystalline polyamide produced by polycondensation of meta-xylylenediamine (MXDA) with adipic acid. This specialty polyamide has lower water absorption and moisture permeability, greater strength and elastic modulus and higher glass transition and heat deflection temperature than standard Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6. It also has superior gas-barrier properties against oxygen and carbon dioxide which can exceed those of many copolymer resins inclusing ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH), vinylidene chloride (PVDC), and acrylonitrile (PAN). On the downside, it has lower impact strength, higher density, and much lower tensile elongation than standard Nylon.1
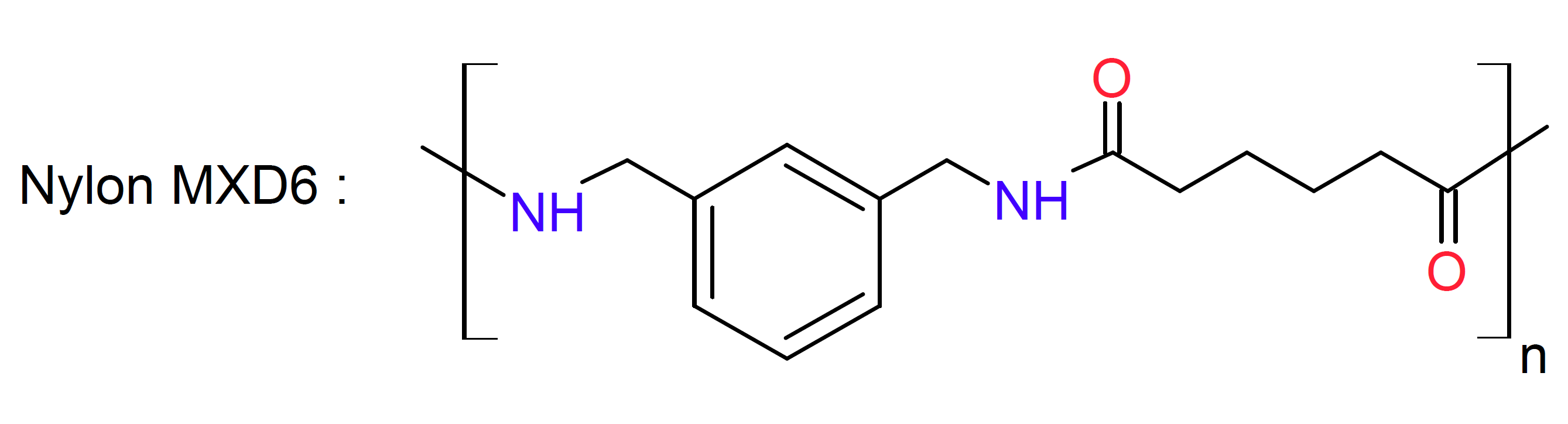
PA-MXD6 also possesses excellent flowability, dimensional stability and creep resistance. It is suitable for processing by injection molding and extrusion and can be cast with excellent surface finish. PA-MXD6 can be blended with a number of other resins to improve their performance properties such as their gas-barrier characteristics.2
PA-MXD6 and its blends are used in several industries, especially in the automotive, electrical, textile and consumer industries. One of the most important applications of PA-MXD6 is food packaging; due to its excellent barrier to gases, it is often co-injection or co-extrusion molded to produce laminated containers, bottles, and packaging sheets with superior gas barrier. Its high strength and stiffness in thin-wall molded parts makes it also suitable for more complex and demanding parts such as door handles, electronic device housings and headlamp surrounds.
Manufacturers |
Brand Names |