Polyvinylidene Dichloride (PVDC)
Properties and Applications
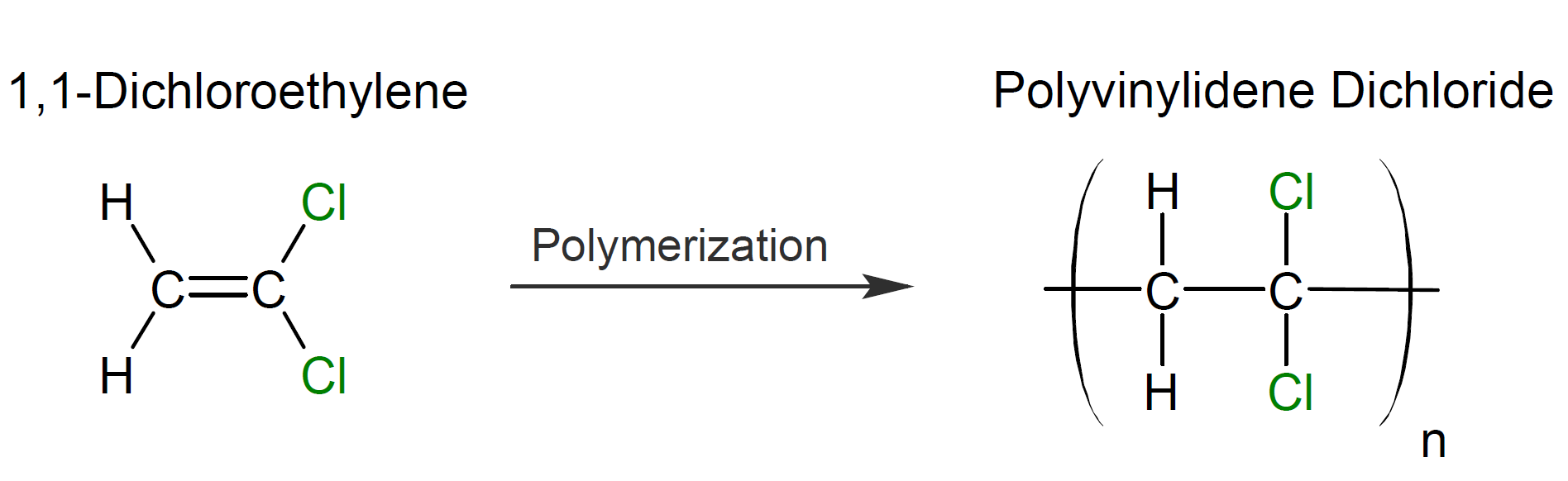
Polyvinylidene dichloride (PVDC), also called polyvinylidene chloride, is a clear, semi-crystalline thermoplastic produced by addition polymerization of 1,1-dichloroethylene.
Films made from PVDC are optically clear, have high degree of gloss and low gas permeability, and are resistant to many chemicals. It also has excellent cling properties, which makes it a good choice for food wrap applications. Because of its higher cost, PVDC is often copolymerized with other monomers or is applied as a thin coating or laminate to improve the properties of cheaper base films. PVDC is known for its excellent gas barrier properties against water, oxygen and many gases (aromas). It also has better corrosion resistance than PVC due to its higher chlorine content and is sometimes copolymerized with vinyl chloride to improve its performance. For example, PVC-PVDC copolymers have improved corrosion resistance and extended service life when compared to ordinary PVC. Films made of these copolymers are known by the tradename Saran (Dow Chemical Co.).
PVDC is mainly used in packaging of food, drugs, cosmetics, and
other perishable or delicate products to extend shelf life. In
comparison with many common films, PVDC coated films have superior
gas and moisture barrier properties, and excellent heat sealability.
These films often compete with acrylic, and PVOH coated films.
PVC-PVDC copolymers or blends are sometimes used in gasoline
filters, valves, and pipe fittings.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |