Glycidyl Amine Epoxy Resins
Properties and Applications
Glycidyl amine epoxy resins (GAER) are high-performance multifunctional epoxies produced by the reaction of aromatic amines with epichlorohydrin. Two common glycidyl amine epoxy resins are triglycidyl para-aminophenol (TGPAP) and triglycidyl of 4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenol (TGAPP). These highly reactive resins, when fully crosslinked, possess high thermal and chemical resistance, a high glass transition and heat deflection temperature, and outstanding mechanical properties. They also possess a lower room temperature viscosity compared to standard epoxy which facilitates handling and processing.
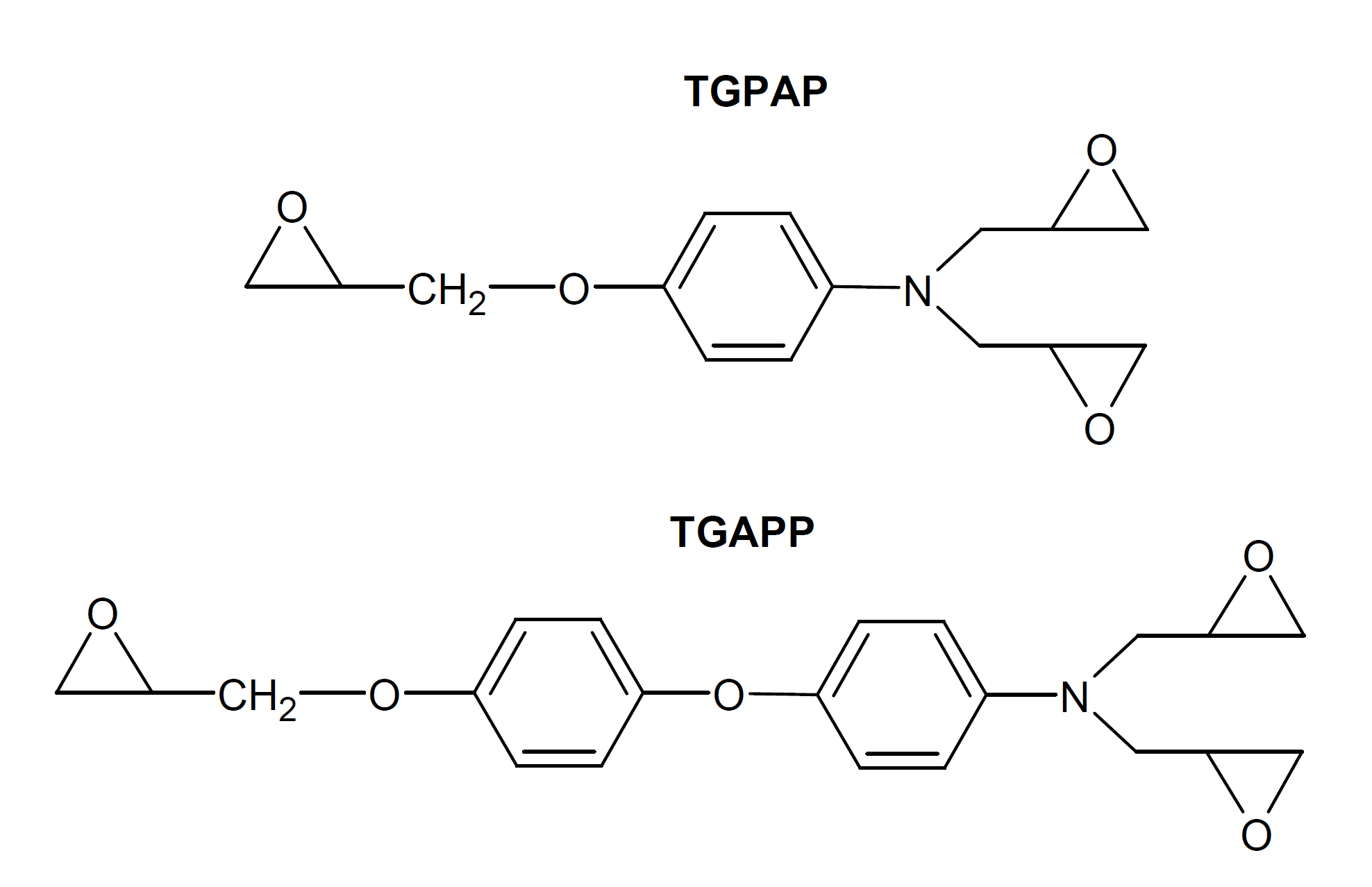
Due to their outstanding thermal stability, good adhesion strength, and low viscosity glycidyl amine epoxy resins are increasingly used in the manufacture of high-performance composites, adhesives and coatings that find several applications in the aerospace and aircraft industries. However, fully crosslinked glycidyl amine epoxy resins are rather brittle which limits their applications when higher impact strength is required. To improve their toughness, GAEs are blended with thermoplastic resins, such as polyether sulfone, polyetherimides and poly(ether ketone).1 Due to their low viscosity, they can also be used as reactive diluents for more viscous engineering thermoplastics.