Polyethersulfone (PES)
Properties and Applications
Polyethersulfone (PES) is an amorphous, highly heat-resistant and transparent thermoplastic synthesized by nucleophilic aromatic substitution between dichlorodiphenyl sulfone and the sodium salt of 1,4-dihydroxybenzene with elimination of sodium chloride. This method yields a non-crystalline resin of slightly amber color. Its good melt stability permits fabrication by conventional thermoplastic processing methods including injection molding, extrusion, solution casting and sintering.
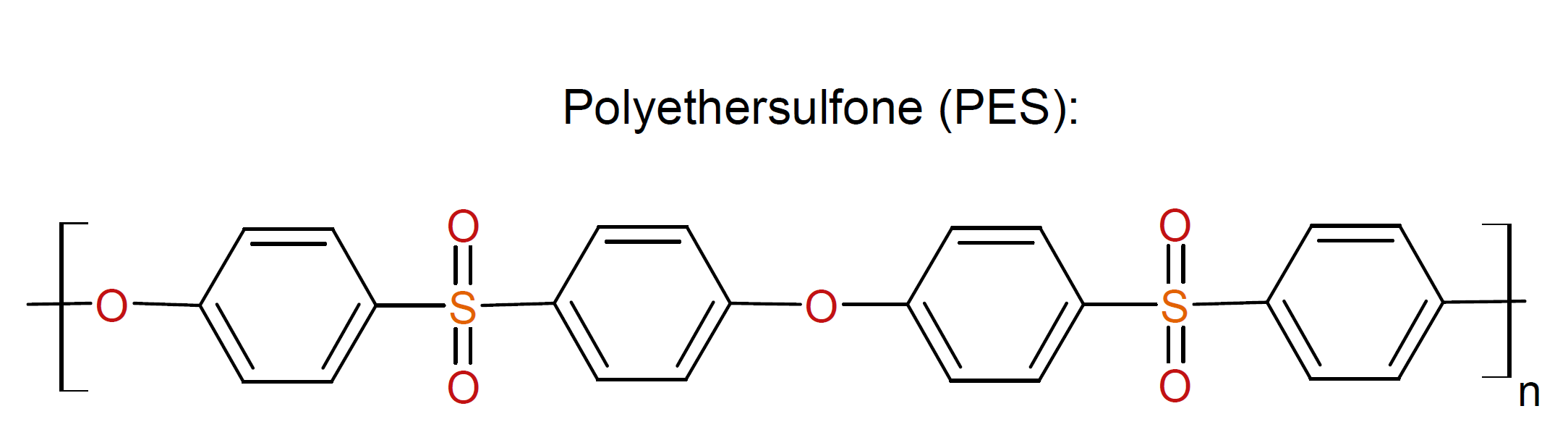
PES is known for its outstanding toughness, high flexural and tensile strength and excellent resistance to chemicals and heat.1 It is typically not attacked by mineral- and silicone-based oils, dilute acids and bases but it is affected by polar solvents such as acetone, chloroform and the like.2
PES is often an excellent choice for components that are exposed to high temperature and corrosive media. Examples include printer cartridges, internal components of coffee machines and battery containers. Polyethersulfone is also used in the automotive and aerospace industries for applications where superior thermal and mechanical properties relative to conventional resins are required. However, most (unfilled) grades are not suitable for outdoor uses because PES has poor weathering, ozone and UV resistance.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |