Polyetherimides (PEI)
Properties and Applications
Polyetherimides (PEI) are an important class of high performance engineering thermoplastics that compete with poly-ketones, polyamideimides, and polysulfones in many engineering applications. They are either prepared by condensation polymerization of an aromatic ether diamine (e.g. 4,4-oxdianiline) and aromatic dianhydride or by a nitro-displacement reaction involving bisphenol A, 4,4′-methylenedianiline, and 3-nitrophthalic anhydride.
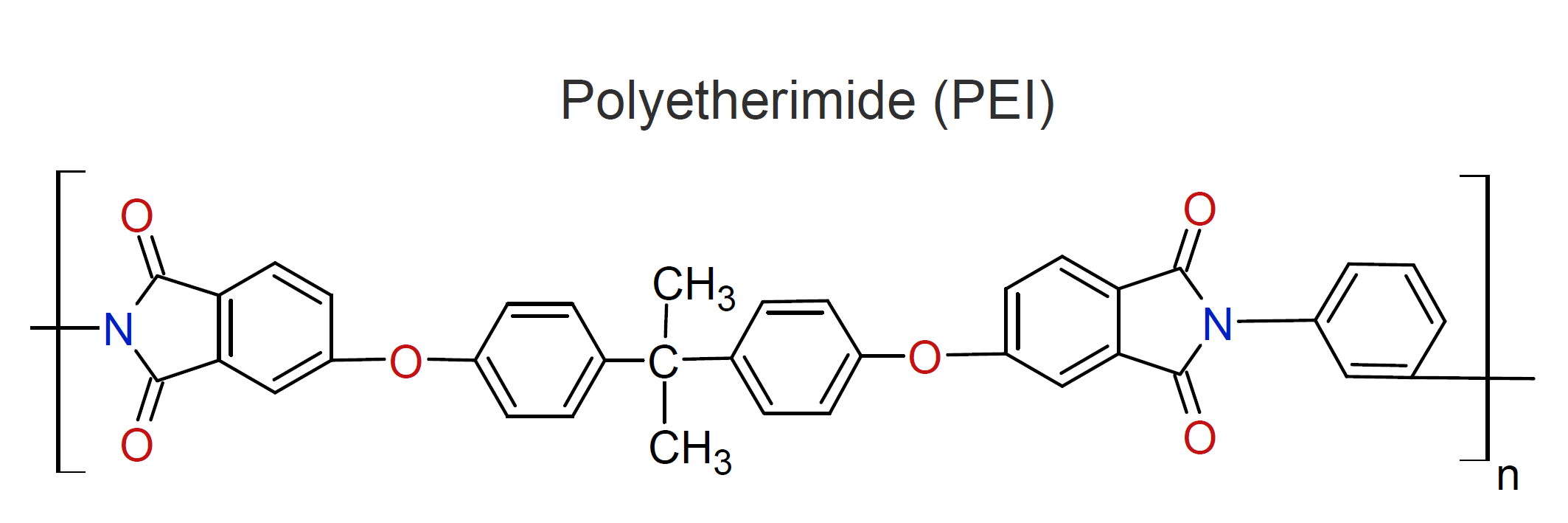
The aromatic ring structure along the polymer backbone improves the thermal, mechanical, and
chemical properties whereas the introduction of flexible aromatic ether linkages improves melt processabiliy and toughness (impact strength).
PEI resins are available in transparent and opaque custom colors, unreinforced as well as carbon or glass (fiber) filled.
The most common polyimides are synthesized from pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4-diamino diphenyl
ether or similar etherdiamines (Kapton type). Most grades can be molded with conventional molding methods such as injection,
compression or blow-molding. However, high processing temperatures
are required due to the high melting or softening point (about 350 - 400°C)1.
PEIs have outstanding thermal, mechanical, and chemical
properties and are often a good choice for very demanding
applications where very high mechanical strength in combination with
high temperature, corrosion, and wear resistance are required. They
resist most chemicals including
hydrocarbons, alcohols and halogenated solvents and have excellent
long-term creep resistance. In many structural applications, they can replace metals
and other high performance materials. Applications include
high-performance parts in the electronic and electrical industry as
well as aerospace and under-the-hood automotive parts.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |