Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid
and
polystyrene sulfonates
Properties and Applications
Poly(4-styrenesulfonic acid), also known as polystyrene sulfonic acid, is an anionic polyelctrolyte (ionomer or polyacid). The linear form is generally water-soluble whereas the cross-linked polymer (called ion-exchange resin) forms three-dimensional structures that swell in water.
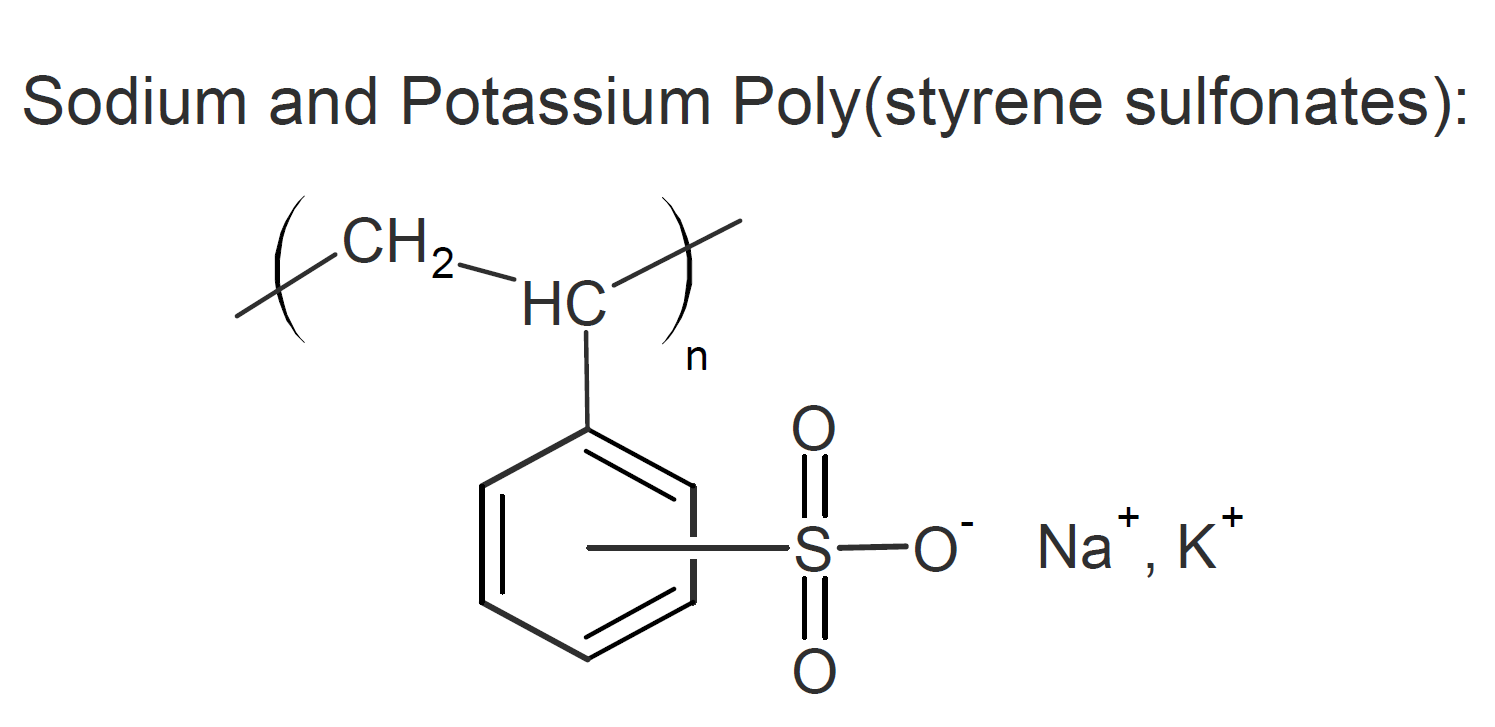
The products of sulfonic acid with a monomeric base, such as sodium or calcium, are highly effective dispersants and cation-exchange resins. Like regular salts, when dissolved in water, they are electrically conductive and like regular polymers, their viscosity strongly depends on the molecular weight and polymer concentration.
Polystyrene sulfonates can absorb large amounts of ions from solutions and are widely used as ion-exchange resins to remove ions such as potassium, calcium, and sodium from solutions in both technical and medical applications. For example, sodium polystyrene sulfonate is often used as a potassium binder that binds potassium ions in the gastrointestinal tract and thereby preventing its intestinal absorption. Besides ion-exchange, polystyrene sulfonate can also be used as a thickener, dispersant agent, conditioner, emulsifier, and clarifying agent. However, often cheaper polyelectrolytes such as carboxymethyl cellulose, polyacrylic acid and their salts are used for these applications.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |