Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)
Properties and Applications
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), also known as cellulose gum or Tylose, and its sodium salt are important cellulose derivatives. The bound carboxymethyl groups (-CH2-COOH) along the polymer chain makes the cellulose water-soluble. When dissolved, it increases the viscosity of aqueous solutions, suspensions and emulsions, and at higher concentration, it provides pseudo-plasticity or thixotropy. As a natural polyelectrolyte, CMC imparts a surface charge to neutral particles and thus, can be used to improve the stability of aqueous colloids and gels or to induce agglomeration.
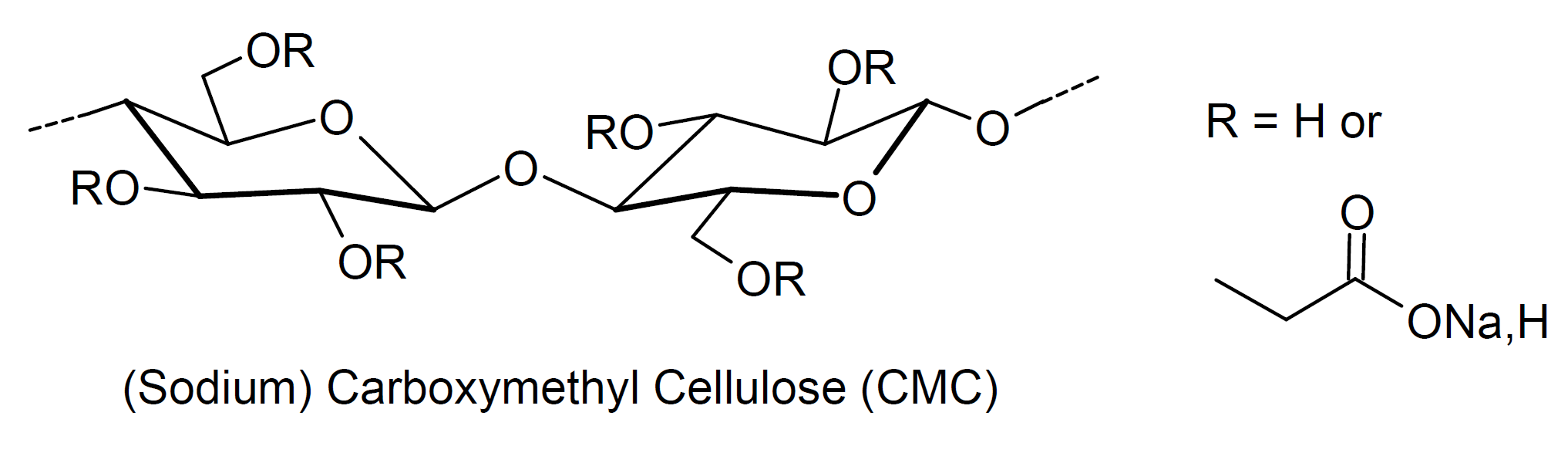
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is used in many products including adhesives, sealants, coatings, textiles, ceramics, mining products, building and construction materials, laundry detergents, pulp, paper, and tobacco. It functions as a dispersant agent, emulsifier, stabilizer, water retainer, thickener and clarifying agent. Or it is used as a film-forming and binding agent, for example to agglomerate and bind iron ore into pellets. Since CMC is physiologically harmless2, it is also widely used in the food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries. In food products, it acts as a thickener, stabilizer and binder and helps to control crystallization, moisture retention, and fat uptake. In cosmetic products such as creams and lotions, it thickens and stabilizes the product and improves its moisturising effect. And in tooth pastes it is added to adjust the viscosity profile.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1According to Grand View Research, the global carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) market reached US$ 1.20 billion in 2016.
2According to U.S. FDA3, sodium CMC is a generally considered safe for human consumption.
3U.S. Food & Drug Administration, 21CFR182.1745, Sec. 182.1745 'Sodium carboxymethylcellulose')