Polyacrylic Acid and Super absorbents
Polyacrylic acid (PAA) is a synthetic high-molecular weight and a watersoluble polyelectrolyte. It finds applications in many industries mostly related to modifying flow, improving stability of aqueous colloids and gels, improving adhesion, and inducing agglomeration.
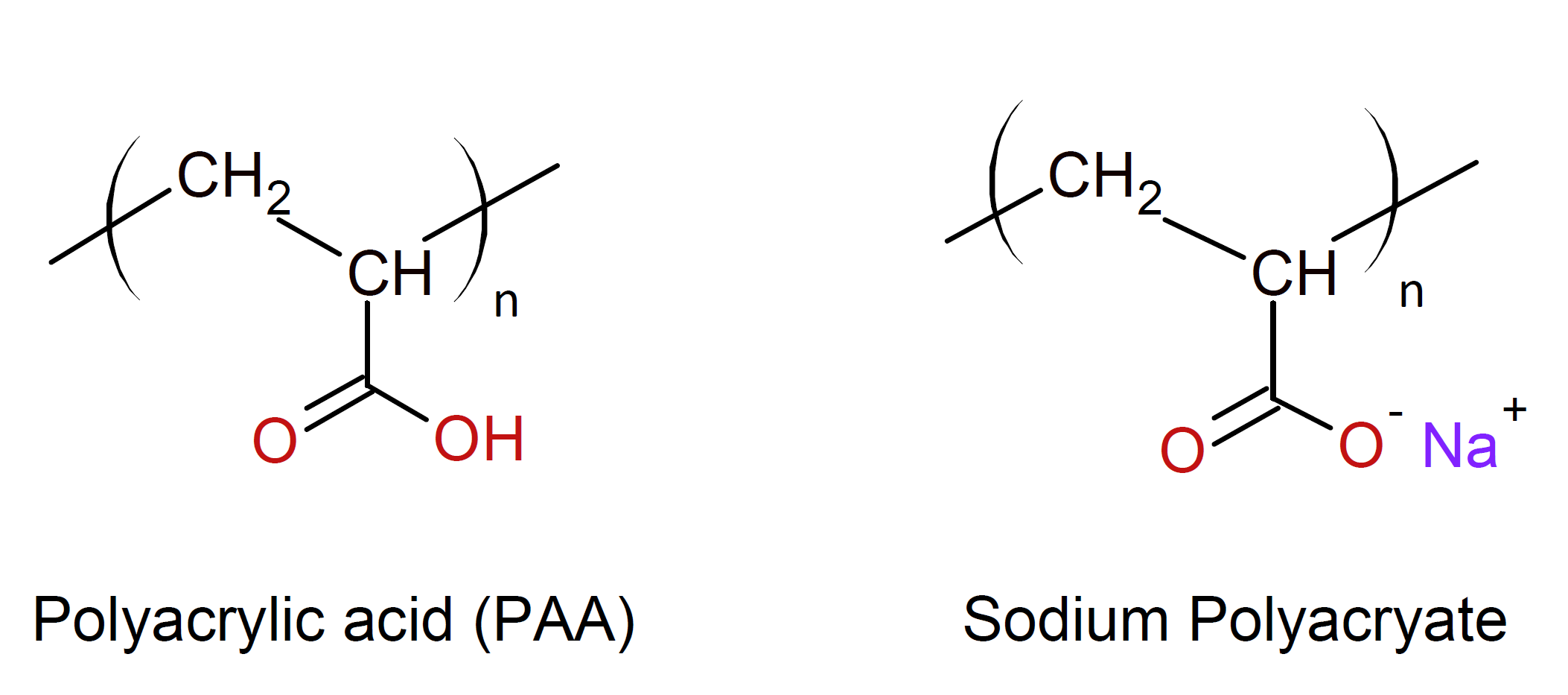
PAAs are used for a wide range of applications including thickeners, dispersant agents, conditioners, emulsifiers, ion-exchanger and clarifying agents.
The monomer itself is frequently copolymerized with other acrylic
resins. It functions as a cross-linker and adhesion promoter in many
formulated products including paints, coatings, adhesives, papers, varnishes and inks.
Because of PAA's water-solubility and biocompatibility, it is
frequently used in biochemical and medical applications such as implant coatings and controlled drug release systems. Large quantities of slightly cross-linked
sodium polyacrylate-polyacrylamide copolymers, called hydrogels, are used as
super absorbents (SAPs).
They can retain (extremely) large amounts of liquid relative to their own mass through hydrogen bonding with water molecules.2 The largest use of SAPs is found in baby diapers and other personal disposable hygiene products such as adult protective underwear and sanitary napkins.1