Polybenzoxazole Fibers
Properties
Polybenzoxazole (PBO) is a high-performance, heat-resistant fiber with a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure. The fiber is almost twice as strong as aramid fibers (Kevlar, Nomex) and about 10 times stronger than steel making it the strongest manmade organic fiber. It also has a 100°C higher decomposition temperature than aramid and exhibits very little creep under stress making it suitable for high continuous loads.
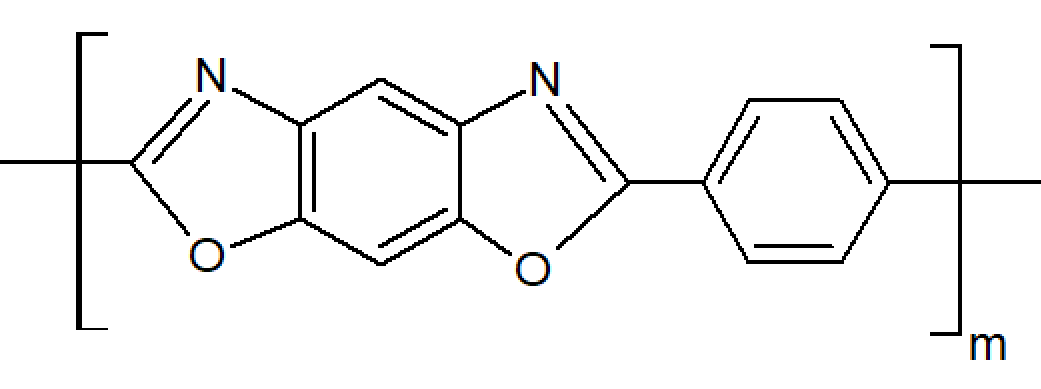
Zylon fibers are produced by a dry-jet wet spinning process. The fiber is difficult to manufacture and rather expensive and thus only used for very demanding applications such as bullet proof vests and expensive sporting goods.
Like aramid fibers, Zylon has an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, even better than carbon and aramid, and outstanding dimensional stability. Due to its fully aromatic structure, it has excellent heat resistance, very low flammability, and good or excellent chemical resistance to most organic solvents. Exposure to strong acids and alkalines, however, causes some strength loss, but when compared with p-aramids its strength retention is noticeably higher1.
COMMERCIAL PBO Fibers
The only manufacturer of PBO fibers is Toyobo which sells the fibers under the tradename Zylon®. It offers two types, AS (as spun) and HM (high modulus). The HM fiber has a higher modulus and lower elongation at break.
Applications
PBO fibers are used for very demanding applications. Its main uses include bulletproof vests; heat resistant garments (safety gloves and firefighter uniforms); high performance sporting goods (bicycle spokes, yacht ropes, rackets, snowboards, and rider suits); and various civil engineering materials.
1Toyobo Zylon Brochure