Differential Scanning Calorimetry
One of the most widely used techniques to measure glass transition temperatures (Tg), melting points (Tm), and heat capacities is differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). This method uses two small identical sample holders; one contains the test sample in a sealed small aluminum pan and the other contains an empty reference pan. The temperatures of the two samples are measured with two identical platinum-resistance thermistors. The differential power needed to maintain the two pans at the same temperature during the heating cycle is then measured as a function of temperature. Instead of differential power, the specific heat (Cp) may be obtained from the measured heat-flow rate by calibration with a reference standard (e.g. saphire) for which the Cp values are accurately known. In the case of an (semi)-amorphous polymer, a discontinuity in ΔCp = Cpl - Cpg is characteristic of a (quasi) second-order Ehrenfest transition, the so-called glass transition temperature (Tg). For many amorphous polymers, the Tg and the heat capacity ΔCp are related by the approximate relationship
Tg X ΔCp ≈ 140 ± 60 J/g (115 J/g)(1)
where ΔCp is the discontinuity of the heat capacity at the Tg.
One of the most important applications of the DSC is the determination of specific heat capacities. The mean error is usually < 2%. The figure below
shows the measured Cp values of polystyrene with a narrow molar mass distribution (heating rate 10 K/min) and various analysis methods. The DSC method can also be used to measure reaction enthalpies and reaction rates.
Heat Capacity of Polystyrene
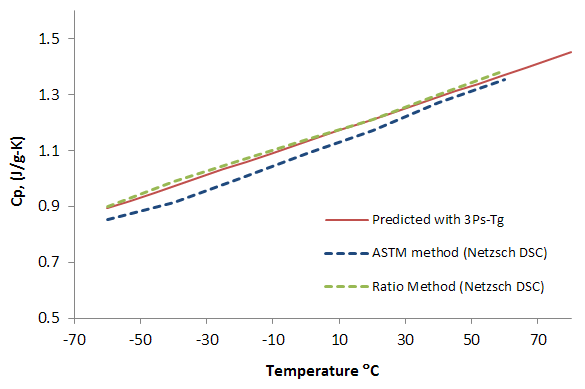
Heat Capacity of Polystyrene
Since most materials show some kind of transition, DSC instruments are used in many industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, agriculture, electronics, polymers, coatings and adhesives.
The biggest advantage of DSC is the ease of use and the quick measurement.
References
- R. Simha, R.F. Boyer, J. Chem. Phys., 37, 1003 (1962)