Poly(ether)sulfones
Properties
Polysulfones, also called polyaryl sulfones, are a class of engineering polymers with high thermal, oxidative and hydrolytic stabilitiy. They are amorphous, transparent thermoplastics that can be molded, extruded, or thermoformed into a wide variety of shapes.
The high thermal stability is provided by the diphenylene sulfone group. It imparts high strength, high resistance to oxidation, and excellent flame retardancy but makes the polymer rigid. Flexibility in the backbone of the polymer is provided by ether linkages. These ether linkages also add to the thermal stability. Many commercial grades can tolerate high temperatures for a long period of time. Some grades, like polyphenylsulfone, are extremely tough and have very high impact strength, comparable to polycarbonate.
Polysulfones are highly resistant to aqueous mineral acids, bases, and oxidizing agents and are fairly resistant to many non-polar solvents. However, polysulfones are not resistant to low polar solvents, such as esters, ketones, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
The usual grades have a good melt stability which permits fabrication by conventional thermoplastic processing methods including injection molding, extrusion and thermoforming. Due to low mold shrinkage, polyethersulfone can be formed into small parts with tight dimensional tolerances.
Synthesis
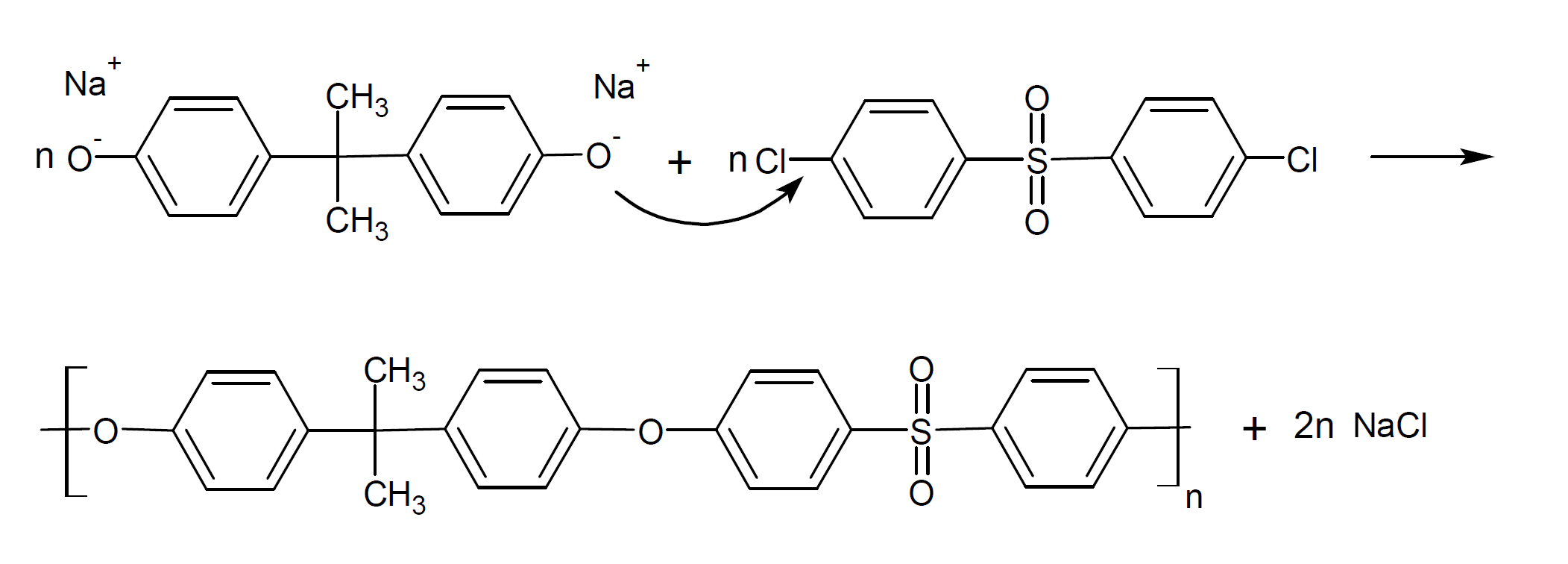
Polyethersulfones can be prepared by polycondensation of suitable monomers or by ring-opening polymerization of cyclic ethersulfones. One of the most common methods is nucleophilic substitution of an aromatic chloro- or fluorosulfone by a phenoxide ion. For example, the reaction of the disodium salt of bisphenol A with dichlorodiphenyl sulfone yields Bisphenol A polysulfone (PSU):
COMMERCIAL Polysulfones
Commercial grades of unfilled and glass-reinforced polysulfones are available from BASF and Solvay. The unfilled (opaque or transparent) grades are available in a range of melt viscosities which are sold in pellet and powder form.
| Polysulfone | Structure of Repeat Unit | Trade Name |
| Polysulfone (PSF, PSU) |
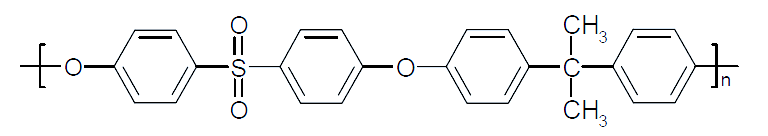
| Udel®, Ultrason® S, Eviva®, RTP PSU |
| Polyethersulfone (PES) |
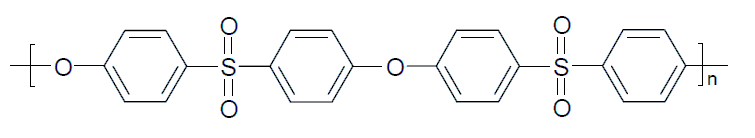
| Ultrason® E, LNP™, Veradel®PESU, Sumikaexce, |
| Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU, PPSF) |
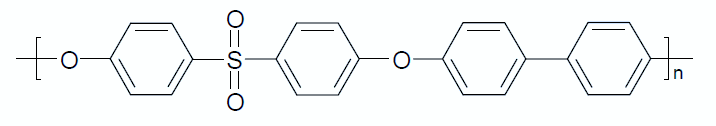
| Radel®, Veriva®, Ultrason® P |
Applications
Polysulfones are chemical inert, highly biocompatible, and can be sterilized. These properties make them highly suitable for medical and food/beverage contact applications. Many grades can withstand long term exposure to hot chlorinated water and have received approval for food contact and drinking water.
Polysulfones are an excellent choice for many machine and appliance parts that are exposed to high temperatures and/or corrosive media. Examples include internal components of coffee machines, battery containers, and printer cartridges. Polysulfones are also used in the automotive and aerospace industries for applications where superior thermal and mechanical properties relative to conventional resins are required.
Some modified polysulfones have a high gas permeability and permselectivity and have found use as membrane materials for gas separation.