Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene (CSM, CSPE)
Properties and Applications
Chlorosulfonated polyethylene (CSM, CSPE), also known as Hypalon®, can be considered a superior type of chloroprene, having better heat and chemical resistance. CSM grades usually contain 20 - 45 percent chlorine which provides excellent resistance to ozone, UV, weathering, and chemicals. This includes oxidizing agents, hot water, and corrosive chemicals. It also has good resistance to dry heat up to 150°C, low flammability, low gas permeability, and good electrical properties. However, it has poor to fair fuel resistance and its low temperature properties are generally limited, depending on the chlorine content of the CSM grade.
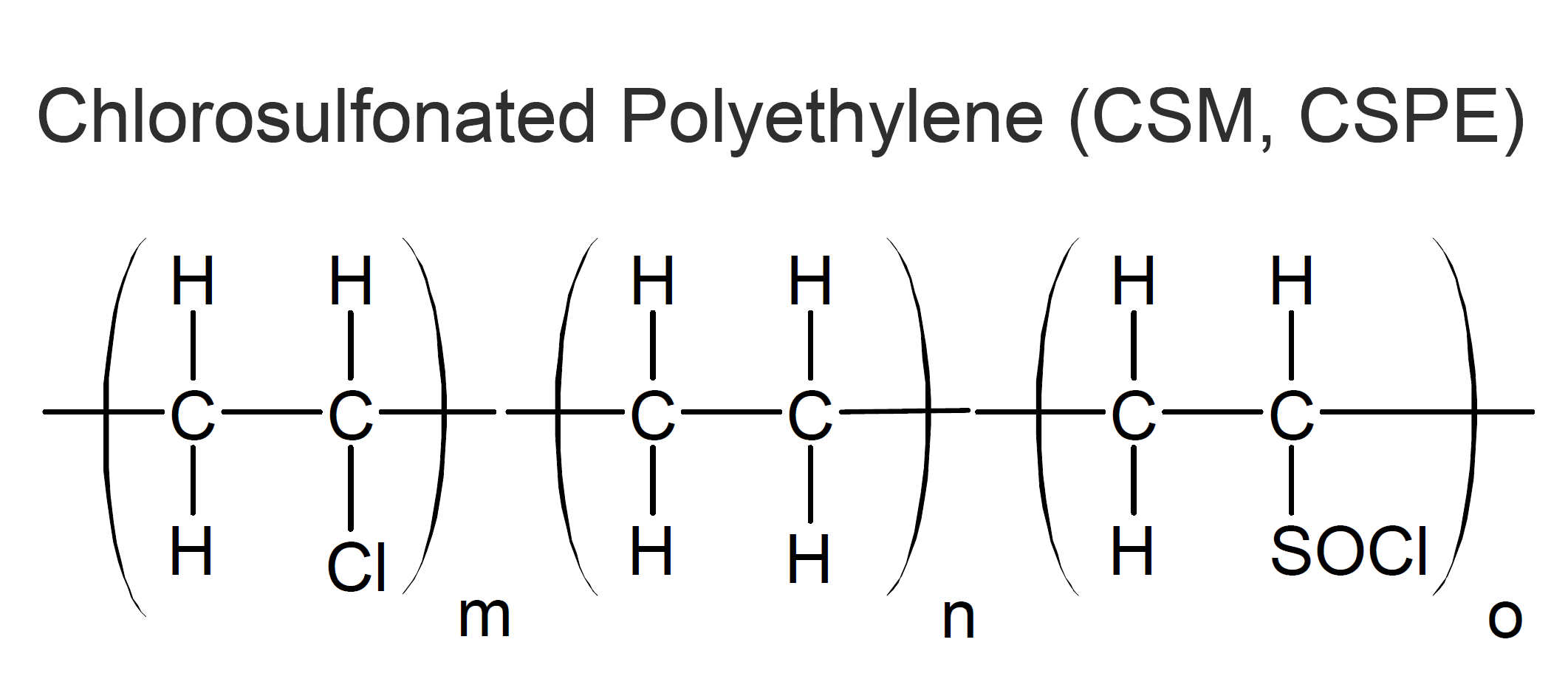
Many of the properties of chlorosulfonated polyethylene are similar to those of chlorinated polyethylene (CM). Their advantage is faster cross-linking (vulcanization) with compounds such as multifunctional amines and peroxides.
CSMs are used in electrical applications such as electrical cable jacketing and in protective coatings against corrosive environments. Its excellent UV stability makes it an excellent choice for outdoor applications like roof sheeting and pond liners. Other applications include acid resistant tank linings, and static seals as well as chemical and heat resistant membranes, fabrics, and hoses. The typical working temperature range is between -20°C and +125°C. CSMs are also added to acrylic adhesive and primer formulations to accelerate cure and improve adhesion.
Manufacturers |
Brand Names |