Polyadipates Polyols
Properties and Applications
Polyadipates are aliphatic, medium to ultra-high molecular weight polyesters formed from polyalcohols and adipic acid bny polycondensation. These linear or lightly branched polyester polyols have a low melting and glass transition temperature, high resistance to solvents and flames, but poor hydrolytic stability. Three common polymeric adipates are polyethylene adipate, polypropylene adipate, and polybutylene adipate.
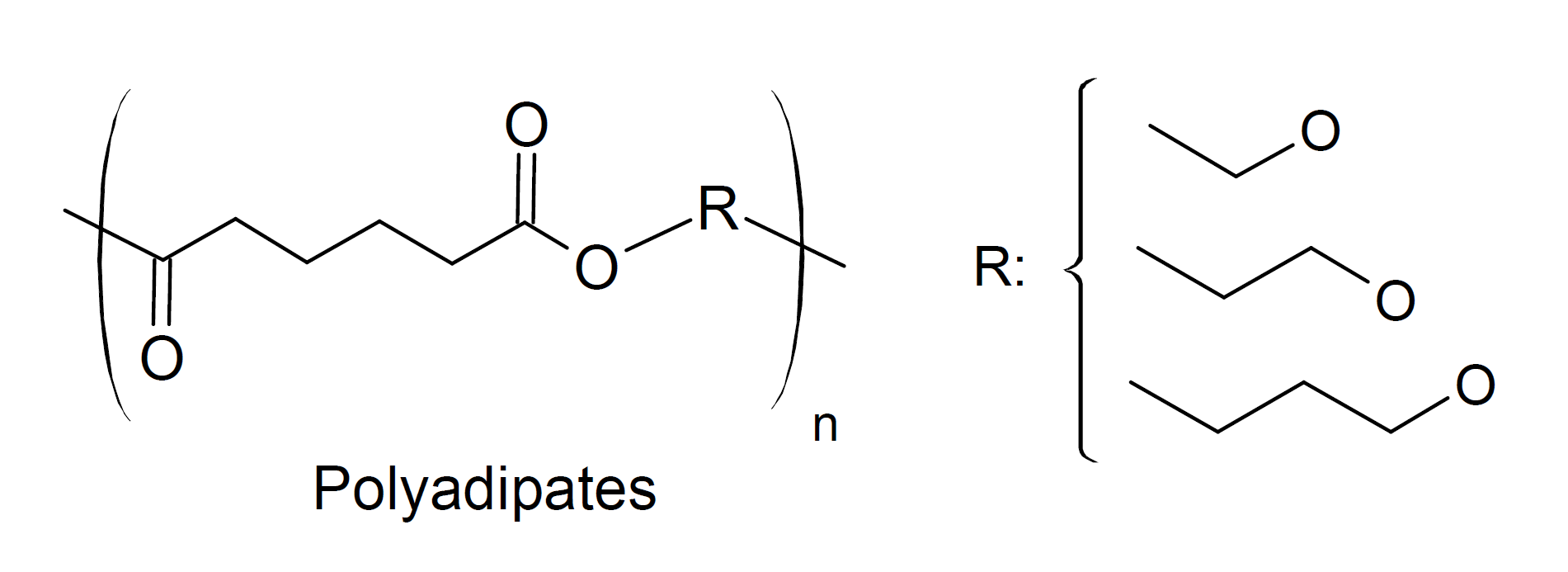
They are mainly used as high-molecular-weight plasticizers and as prepolymer reactants in the synthesis of polyurethanes. When added to or copolymerized with thermoplastics, they impart flexibility, reduce melt viscosity, and lower the elastic modulus and glass transition temperature. They also improve resistance to abrasion of thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPUs) in coating and footwear applications.
Polyadipates are added to many plastics and rubbers, including thermoplastic PU, PVC, NR, NBR, and PVA. They are chosen over low MW plasticizers when very low plasticizer migration and/or extended product durability is required.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |