Polysulfone (PSF, PSU)
Properties and Applications
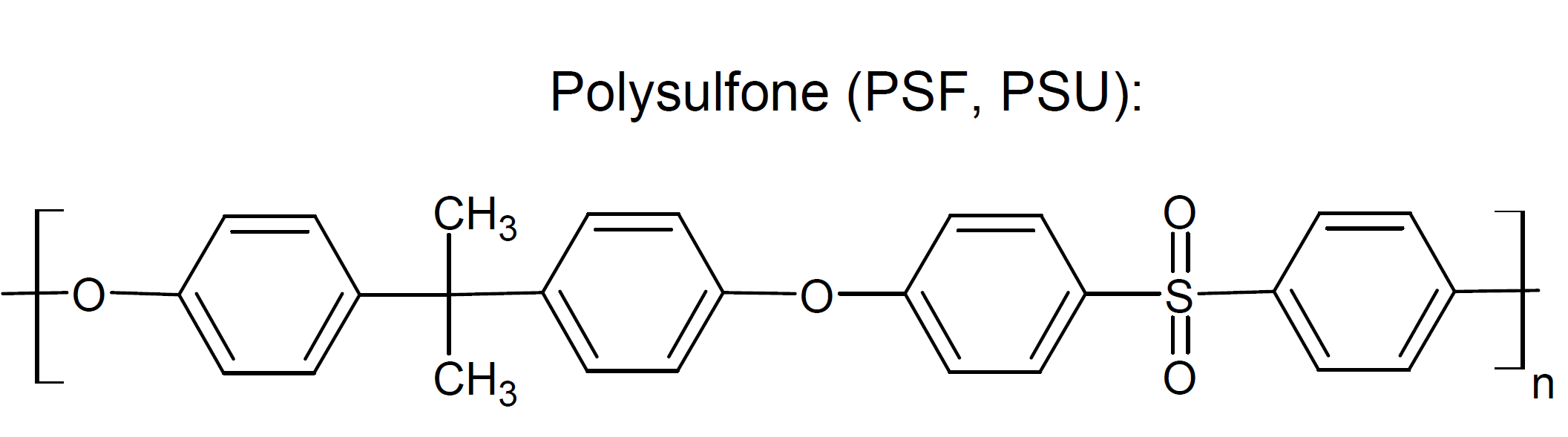
Polysulfone (PSF, PSU) is an amorphous, transparent, and pale amber high-performance thermoplastic produced by nucleophilic aromatic substitution between dichlorodiphenyl sulfone and disodium salt of bisphenol A with elimination of sodium chloride. The resulting resin exhibits good melt stability which permits fabrication by conventional thermoplastic processing methods including injection molding, extrusion and thermoforming. Due to its low mold shrinkage, it can be formed into small parts with tight dimensional tolerances.
PSF has outstanding mechanical, electrical and thermophysical properties. Many commercial grades can tolerate high temperatures for a long period of time and have very high and tensile strength and impact strength comparable to polycarbonate. Polysulfone also exhibits excellent chemical and hydrolytic stability. For example, it is highly resistant to aqueous mineral acids, bases, and oxidizing agents and is fairly resistant to many solvents. However, PSF is not resistant to aromatic and several moderate polar solvents such as benzene, toluene, methyl ethyl ketone, and chlorinated hydrocarbons.1
Polysulfone is often an excellent choice for components that are exposed to steam and hot water. Examples include faucet components, internal components of coffee machines, sterilizable plastic parts like medical devices, hot water fittings, and plumbing manifolds, as well as membranes for water treatment, gas separation, hemodialysis, food and beverage. However, (unprotected) polysulfone is not recommended for outdoor uses because most (unfilled) grades have poor weathering and UV resistance.2
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |