Polyphenylene Sulfides (PPS)
Properties and Applications
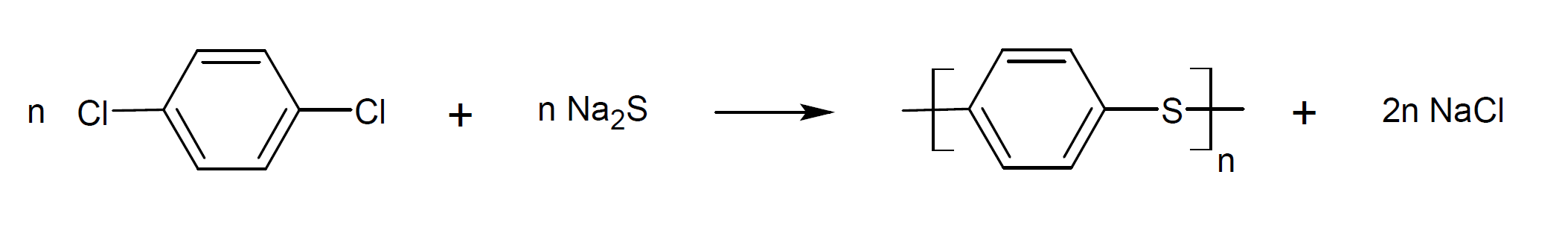
Polyphenylthioether, also called polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), is a semicrystalline, high-performance, engineering thermoplastic produced by the reaction of p-dichlorobenzene with sodium sulfide.
It has outstanding heat
and chemical resistance, good dimensional stability, and high mechanical strength due to the aromatic
benzene
rings in the polymer backbone covalently linked by a single electronegative sulfur atom.
The fully aromatic ring structure is also responsible for the good retention of mechanical properties and dimensional stability at elevated temperature.
On the downside, most grades are difficult to process due to
their poor solubility in most solvents and high melting point (287°C / 550 °F). For example,
a typical moderate-molecular-weight grade has to
be injection molded at 310 - 340°C (590 - 645°F). The molded parts can
be crosslinked by air aging to yield totally insoluble plastics.
PPS is often reinforced with glass fibers or mineral fillers to further improve its
(high-temperature) performance. These grades have higher tensile strength, are noticeably
stiffer (higher modulus), and exhibit better strength retention at elevated temperature (higher heat deflection temperature)
than unfilled grades.
PPS is used for electrical and electronic parts such as plugs, connectors, housings, relays, switches and many other electrical and electronic insulators. In the automotive and chemical industry, PPS is used for air intake systems, pump parts, gaskets, valves, bushings, and bearings, particularly for service in corrosive environments.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |