Polybenzoxazoles (PBO)
Properties and Applications
Polybenzoxazoles (PBO) are a novel class of extremely heat-resistant thermoplastics with a benzene-fused oxazole ring structure. The most important benzoxazole is poly(p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole) which is sold under the trade name Zylon.1 The chemical structure of this polymer is shown below.
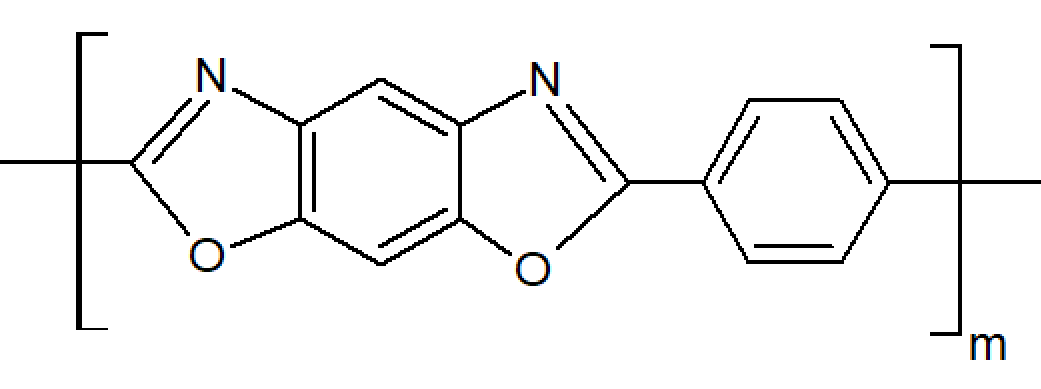
It is one of the highest performing engineering thermoplastics on the market.2 It has a
100°C higher decomposition temperature than aramid and exhibits very little
creep under stress making it suitable for high continuous loads.
However, it is rather expensive and difficult to manufacture.
Polybenzoxazoles is mainly used for the production of high-performance fibers. Like aramid fibers, PBO fibers have an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, even better than carbon and aramid, outstanding dimensional stability, and exceptionally high thermal and chemical stability. Important applications include bulletproof vests, heat resistant garments (safety gloves and firefighter uniforms) and high performance sporting goods such as bicycle spokes, yacht ropes, rackets, snowboards, and rider suits, and various civil engineering materials.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1It is synthesized by
direct condensation and cyclization of 4,6-diamino-1,3-benzenediol dihydrochloride with terephthalic acid (TA) or a derivative of it. Source: H. Lin, Y-D. Huang and F. Wang, Int. J. Mol. Sci, 9, 2159-2168 (2008)
2The tensile strength of PBO is about twice that of p-aramid and 10 times that of PBI. Even after prolonged UV exposure over
the life of the product, PBO maintains higher strength than PBI. Source: TOYOBO CO., LTD. PBO Technical Bulletin F606P.