Polybutylene (Poly(1-butene), PB-1)
Properties and Applications
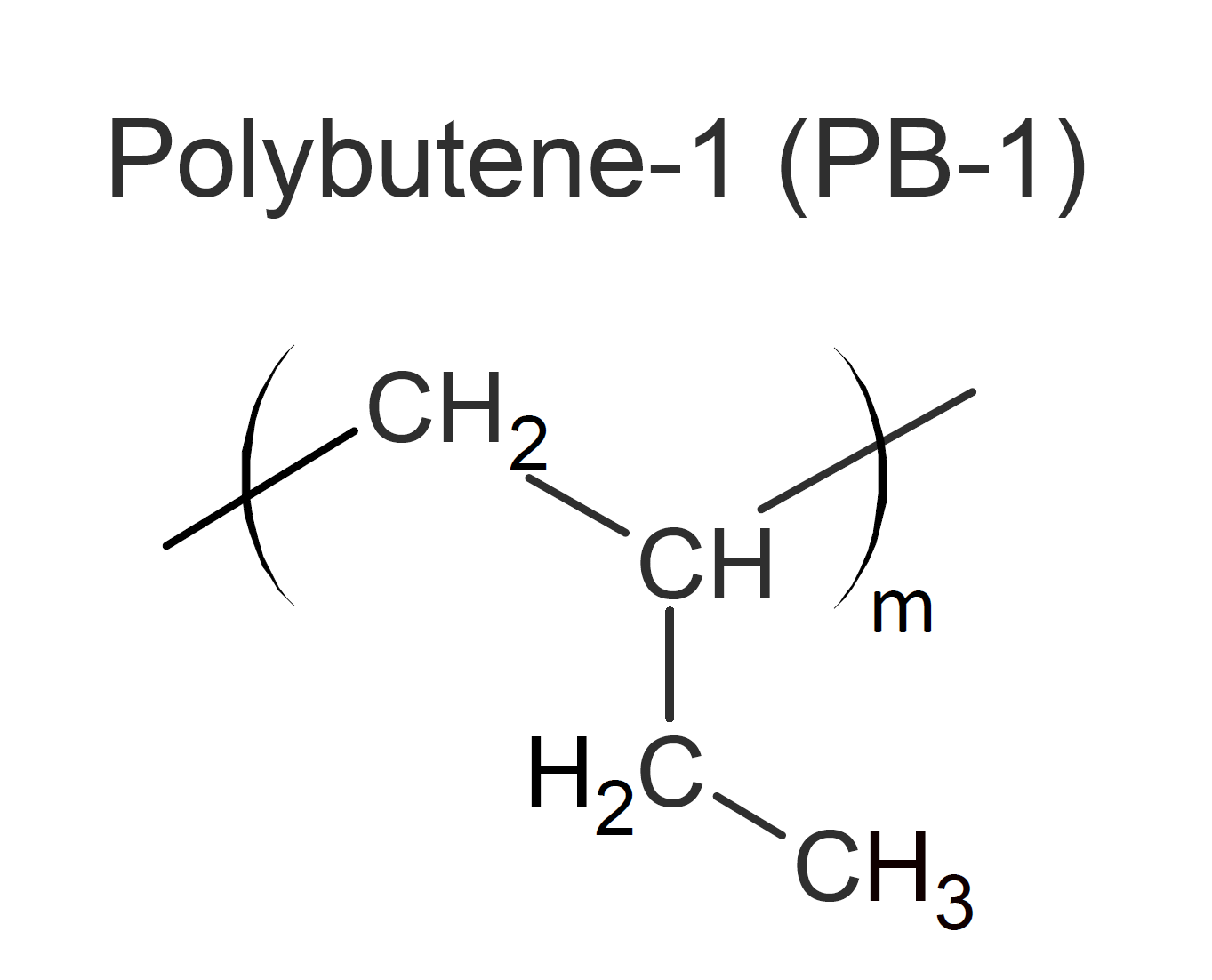
Polybutene (PB-1), also called polybutylene, is a linear, highly isotactic and semi-crystalline thermoplastic, produced by polymerization of 1-butene using stereospecific Ziegler-Natta catalysts. It can be processed and molded with conventional manufacturing equipment and is often blended or (randomly) copolymerized with cheaper polyolefins, such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) to improve and/or taylor their properties. In general, the flexibility, toughness and stress crack resistance increases with increasing 1-butene content in the copolymer.
PB-1 has high strength and flexibility over a broad temperature range and exhibits excellent creep and heat resistance which makes it the preferred polyolefin for more demanding applications. It is typically used when good mechanical properties at moderate to high temperatures are required. Important applications include domestic hot water pipes, hot water heaters and tanks, hot melt adhesives and compression packaging. It is also used in polyolefin blends, predominantly in polyethylene, to tailor its thermal bonding properties and peel strength for consumer and medical packaging. Low molecular weight grades are used in adhesives, sealants, paper laminates etc. to improve tack and peel strength.