Polyamide 12 (Nylon 12)
Properties and Applications
Polyamide 12 (also called Nylon 12, polylaurolactam or polydodecanolactam) is a thermoplastic polymer with the formula [-(CH2)11C(O)NH-]n. It is made from either ω-aminolauric acid or laurolactam, each having 12 carbon atoms. This type of polyamide has excellent impact strength and much lower moisture absorption, melting point and density than the standard Nylon 6 and Nylon 6,6. It is also less sensitive to stress cracking. On the downside, it has lower flexural and tensile strength as well as lower heat deflection and glass transition temperature than standard Nylon.
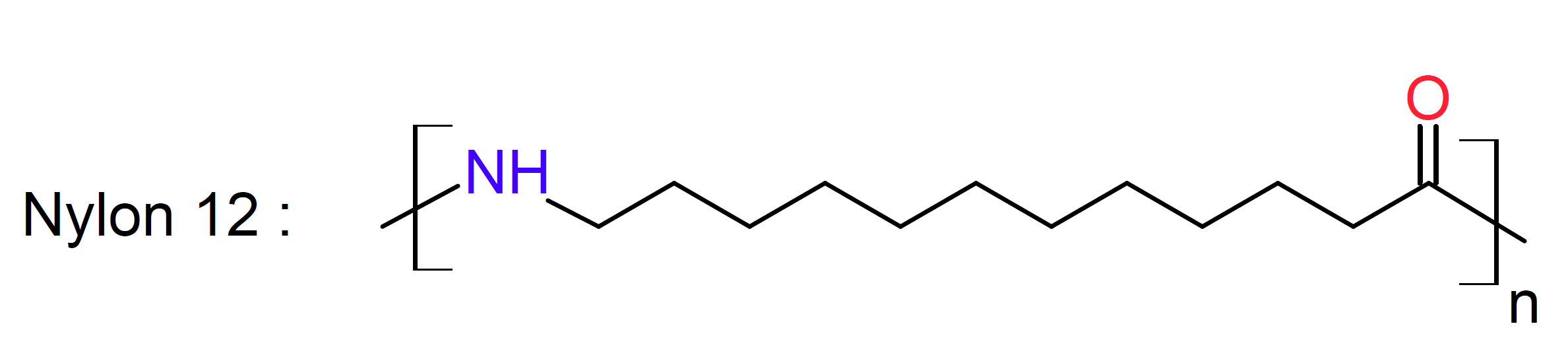
PA12 is sometimes copolymerized with polyetherdiols such as PTHF which further increases the toughness and impact strength, particularly at cold temperatures. The ether blocks in the polymer also improve the resistance to certain chemicals and solvents. This type of elastomeric Nylon is known as polyether block amide (PEBA).1
Nylon 12 and its copolymers is used in many industries, especially in the sport goods, automotive and electrical industries. Important applications include elements of sport shoes and ski boots, sports glasses, interior and exterior designs on automobiles, and permanent antistatic parts such as conveyor belts, electrical housings and paint spray hoses.
Manufacturers |
Brand Names |