Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (HPC)
Properties and Applications
Hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC) is a nonionic thermoplastic cellulose derivative produced by etherification with propylene oxide under alkaline conditions.1,2 This type of modified cellulose is a completely odorless, tasteless, and non-toxic white to slight-yellow powder that is soluble in cold and hot water as well as in many polar organic solvents including methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, acetone, and propylene glycol. When dissolved in water or solvent, it forms a transparent viscous solution which has a non-Newtonian flow behavior. However, HPC displays little to no thixotropy and unlike carboxymethyl cellulose, the viscosity is not affected by the pH because it is non-ionic.
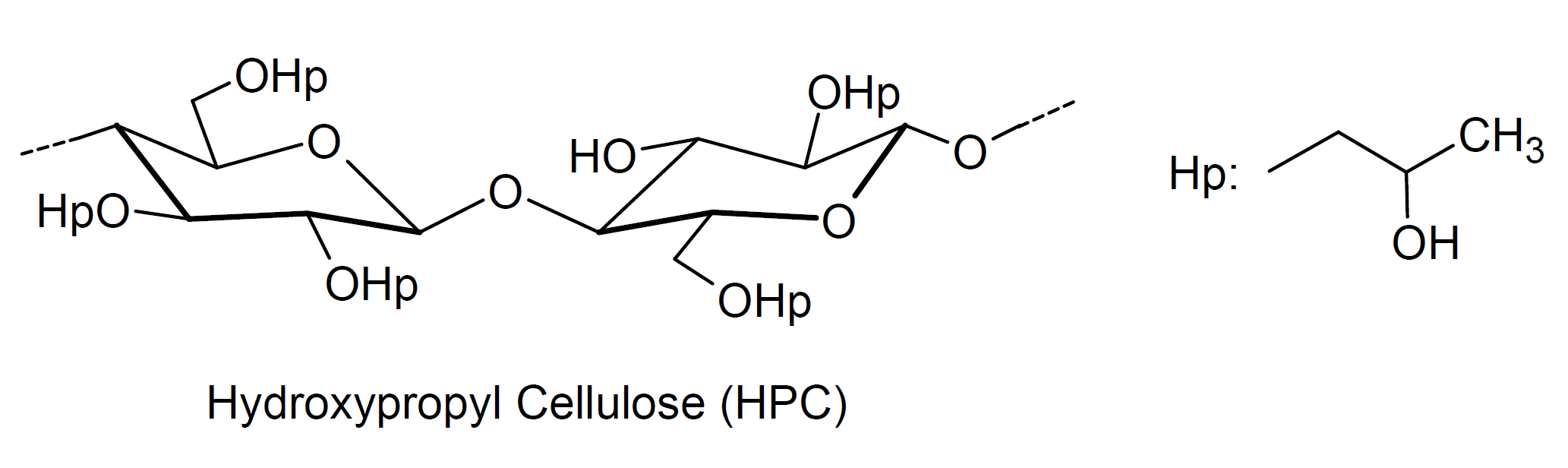
HPC is available in a wide range of viscosities and particle sizes. It is often added to water-based formulations to adjust the viscosity and to stabilize colloids and emulsions. It is also used as a binder and film former in oral and topical pharmaceutical products.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1US Patent 4,292,426; Process of Producing Hydroxypropyl Cellulose, Orii et al. 1980
2The hydroxyl groups formed during etherification reaction can also be etherified. When this occurs, the moles consumed during etherification can be greater than 3 per cellulose ring.