Glycidyl Ethers (Epoxy Modifiers)
Properties and Applications
Glycidyl ether monomers are low molecular weight, mono- or multi- functional epoxy compounds. These functional resins have usually a (much) lower viscosity than standard epoxy resins such as diglycidyl ethers of bisphenol A and F, or epoxy-novolacs. They can be divided mainly in aliphatic, aromatic and cycloaliphatic glycidyl ethers and can be further classified based on their epoxy functionality as mono-, di- and tri-functional. Four common reactive diluents are shown below.
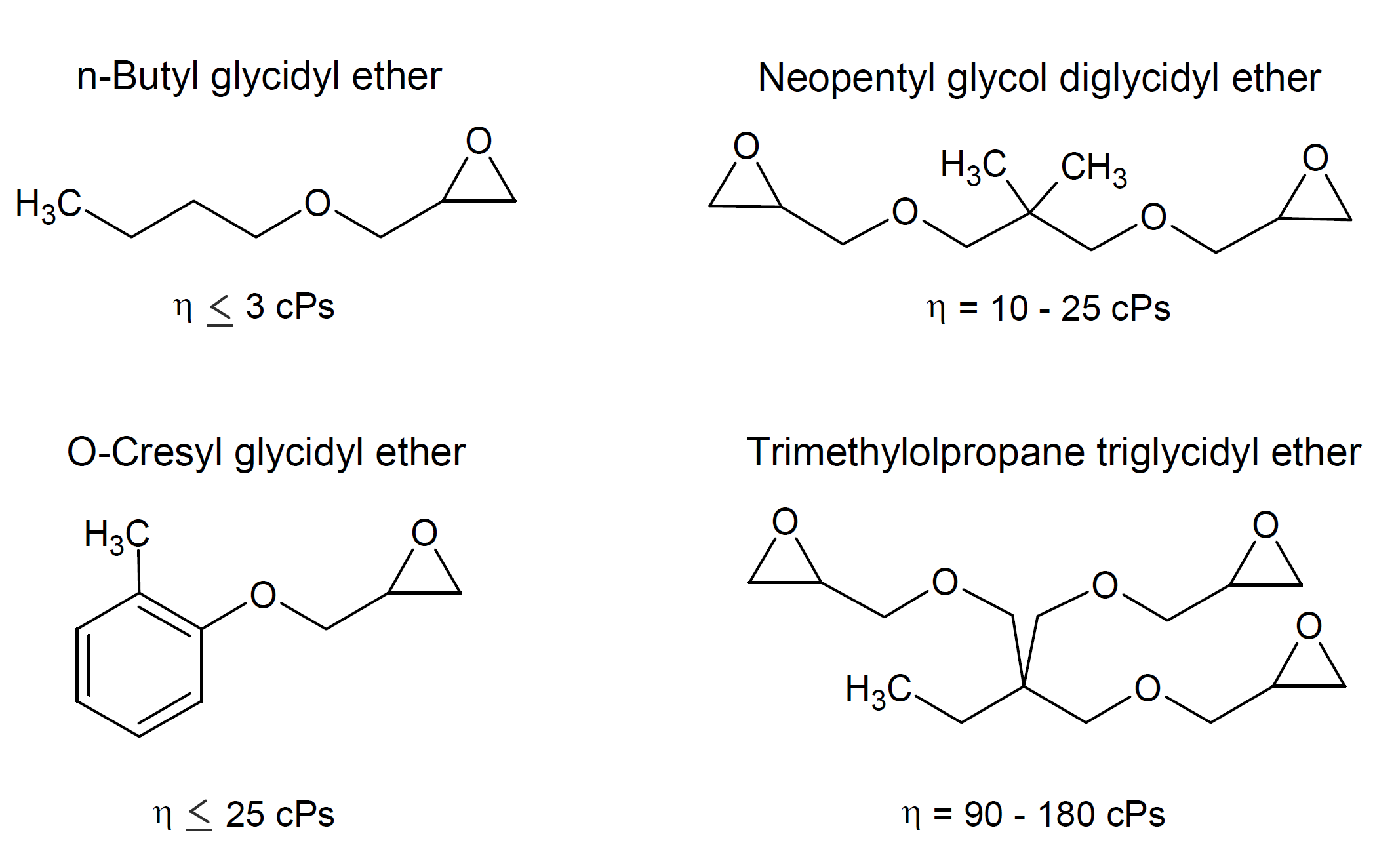
Most of these resins are aliphatic in nature and have a much lower viscosity than standard DGEBA epoxy. Monofunctional diluents have typically the lowest viscosity. These diluents, however, tend to reduce mechanical strength because they terminate growth of the polymer, and thus reduce the cross-link density of the epoxy product which, in turn, reduces high temperature performance. Difunctional diluents, on the other hand, have little effect on cross-link density. They are often a good choice when viscosity reduction with good retention of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures are desired. Trifunctional diluents increase the cross-link density which leads to excellent retention of high-temperature properties and improved chemical resistance. These diluents, however, have a higher viscosity than mono- and difunctional diluents.
Epoxy reactive diluents are used in a variety of products including solvent free paints, coatings and adhesives. They function as reactive diluents to reduce the viscosity of the base resin and as performance modifiers to improve certain properties such as impact strength, flexibility and adhesion of the cured resin product. They also improve ease of processing and/or increase the reactivity of the base resin.