Epichlorohydrin Polyether Elastomers (ECO)
Properties and Applications
Epichlorohydrin rubber (ECO) is a synthetic specialty elastomer produced by ring-opening copolymerization of epichlorhydrin and ethylene oxide. Its properties are very similar to nitrile rubber (NBR) but with better heat and ozone resistance and improved low temperature flexibility. It also possesses much better (inherent) flame retardance due to the high chlorine content which can be further improved by the addition of flame retardant additives. The chloromethyl side groups also provide sites for cross-linking.
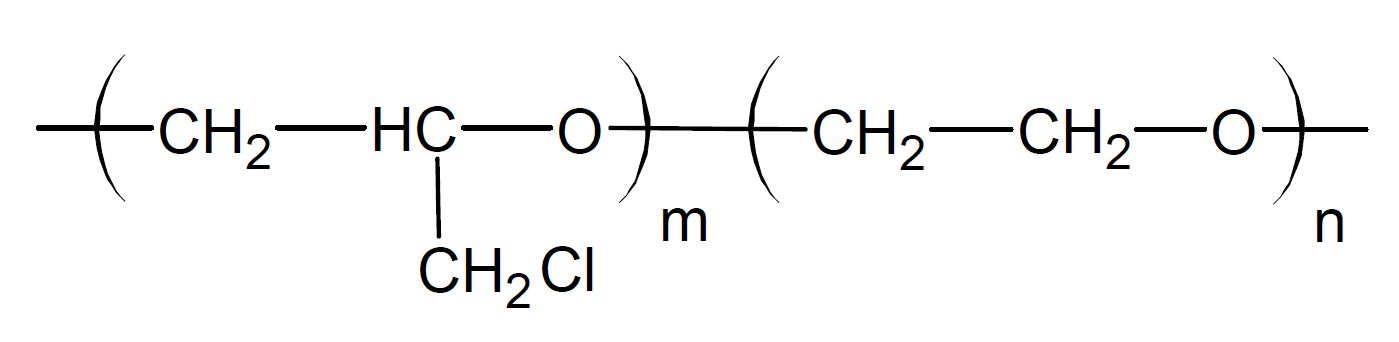
ECO has very attractive elastomer properties. For example. it possesses very low gas permeability, excellent ozone and weather resistance, good compression set and good heat and mineral oil resistance. Its resistance to hydrogen peroxide and alkalis is also good. However, epichlorohydrin rubber is generally unsuitable for use with (wet) chlorine, strong acids and many common polar solvents such as alcohols, esters, ketones, and phosphate ester-based hydraulic fluids. Some other limitations include low abrasion resistance and only moderate low-temperature flexibility (depending on the composition).
Epichlorohydrin elastomers are widely used in the automotive industry for seals, (fuel) hoses, gaskets, O-rings, cable jackets, and belts. They are also an important ingredient of rubber glues. However, they are unsuitable for rubber to metal bonding because of their corrosiveness to metals. The typical working temperature range is about -40°C to +125°C (150°C short term).
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |