Cyclic Block Copolymers (CBCs)
Polycyclohexylethylene (PCHE) - ethylene-co-1-butene (EB)
Properties and Applications
Cyclic block copolymers (CBCs) are a novel group of thermoplastics that are based on fully hydrogenated styrene and conjugated dienes produced via anionic polymerization.1 CBCs have better heat, UV, and chemical resistance than the corresponding non-hydrogenated analogs due to the absence of double bonds. In addition, they have low water absorption, very high transparency, low density, and superb purity. However, hydrogenation also reduces the mechanical performance (elasticity) and increases the cost of the copolymer.
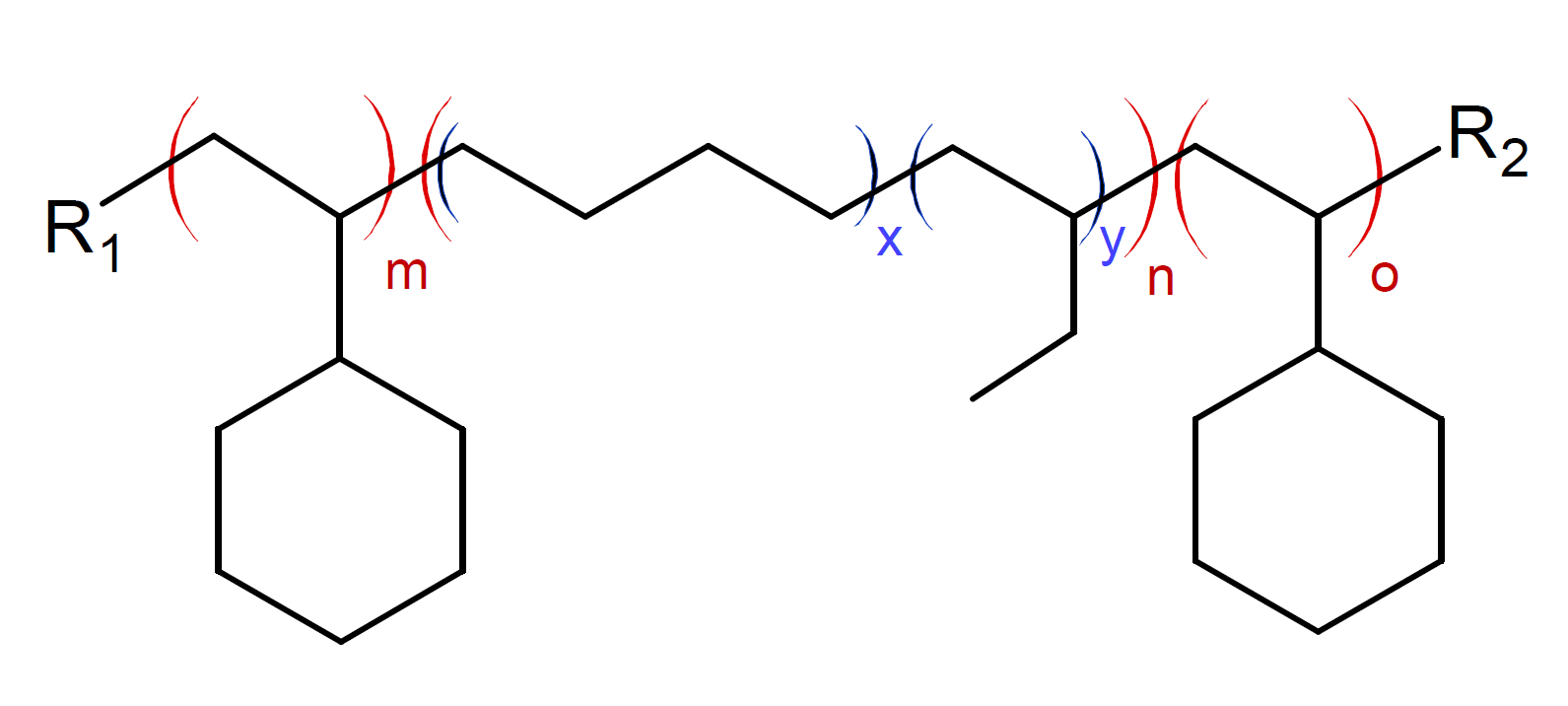
The properties of CBCs can be tailored over a wide range from rigid and hard to very soft and elastic by adjusting the ratio of cyclohexylethylene (CHE) to ethylene-co-1-butene (EB) in the copolymer. Thus CBCs offer great design flexibility for manufacturers and allow for easy processing including injection molding, extrusion, and solvent casting.2
CBCs can be used in many applications where BisA PC, COCs or COPs are used but where improved thermal stability, UV durability and similar or higher transparency, toughness, and / or biocompatibility are required. This includes optical components for LCDs; medical devices such as high cleanness vials and pre-filled syringes; bio-diagnostics such as microplates, curvettes and bio-chips for UV and / or autofluorescence detection; as well as transparent medical, food, and beverage containers that need to be sterilized by boiling water, steam, and/or UV radiation.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1Hydrogenation increases the stiffness
and rigidity of the polymer chain backbone, which, in turn, increases the melting point.
2ViviOn™ Cyclic block copolymers brochure, 2016 USI Corporation