High Vinyl Butadiene Rubbers
Properties and Applications
High vinyl polybutadiene (Vinyl PBD) is a synthetic rubber with more than 70 percent vinyl units. It is produced by anionic polymerization with strong catalyst such as alkyl lithium that results in a mainly saturated backbone with pendant vinyl groups and with small portions of trans and cis PBD. Compared to cis polybutadiene rubber, it has has a much higher glass transition temperature (Tg), and thus is much stiffer. Despite its high Tg, it imparts high rebound resilience within a wide temperature range and when used in tires, it provides a unique balance of low rolling resistance and high wet grip.1,2 However, due to the many pendant vinyl groups, this type of rubber has a much higher viscosity than linear PBD at similar molecular weight.
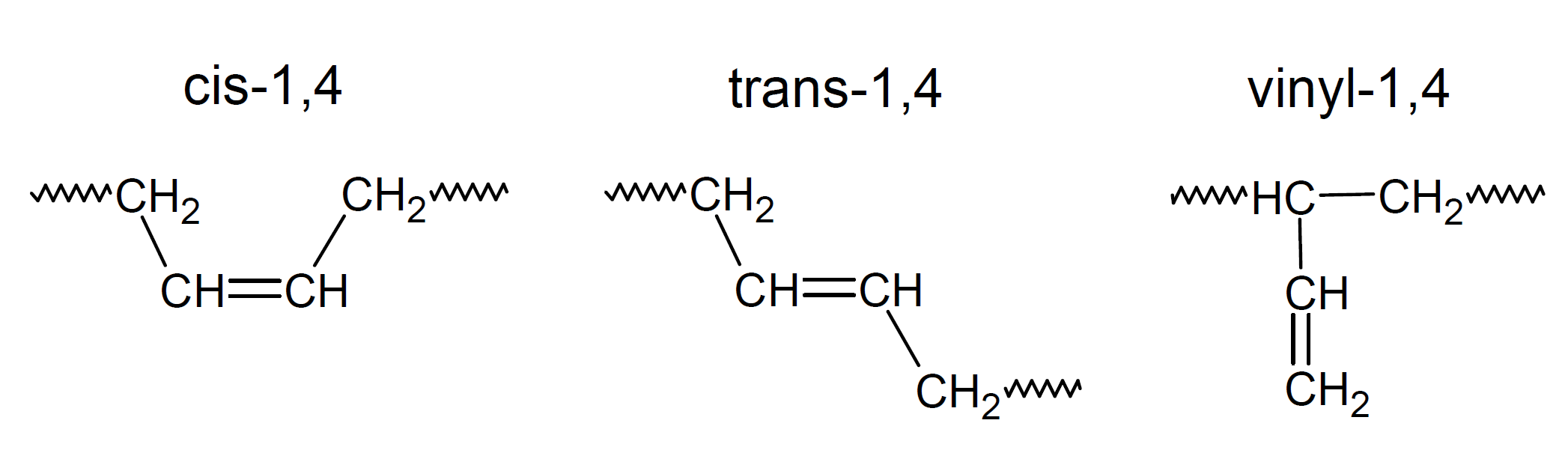
High vinyl polybutadiene is much more reactive than high cis and high trans PBD and can undergo similar vulcanization or free radical cure. Unlike linear PBD it can also be polymerized by UV light and other curatives to which cis and trans polybutadiene is relatively inert.
High-vinly polybutadiene is produced on a much smaller scale than cis polybutadiene. It is mainly used in high quality tires to improve rebound resilience. Vinly PBD is also available in liquid and functionalized form. These types of PBD are used to modify and improve rubber formulations such as adhesion to substrates, toughness, heat resistance, swell resistance and moldability. Other non-rubber uses include coatings, paints, sealants and adhesives.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |