Organophosphorus Resins
(Polyphosphate Esters & Phosphorus-modified Resins)
Properties and Applications
Organo polyphosphates, also known as polyphosphate esters (POPEs), are an important class of organophosphorus compounds. They are produced by reacting a phosphoric acid derivative such as an aryl or alkyl dihalophosphate or a phosphoric anhydride with a diol or diol prepolymer.1 The general chemical structure of these (organo)phosphorus resins is
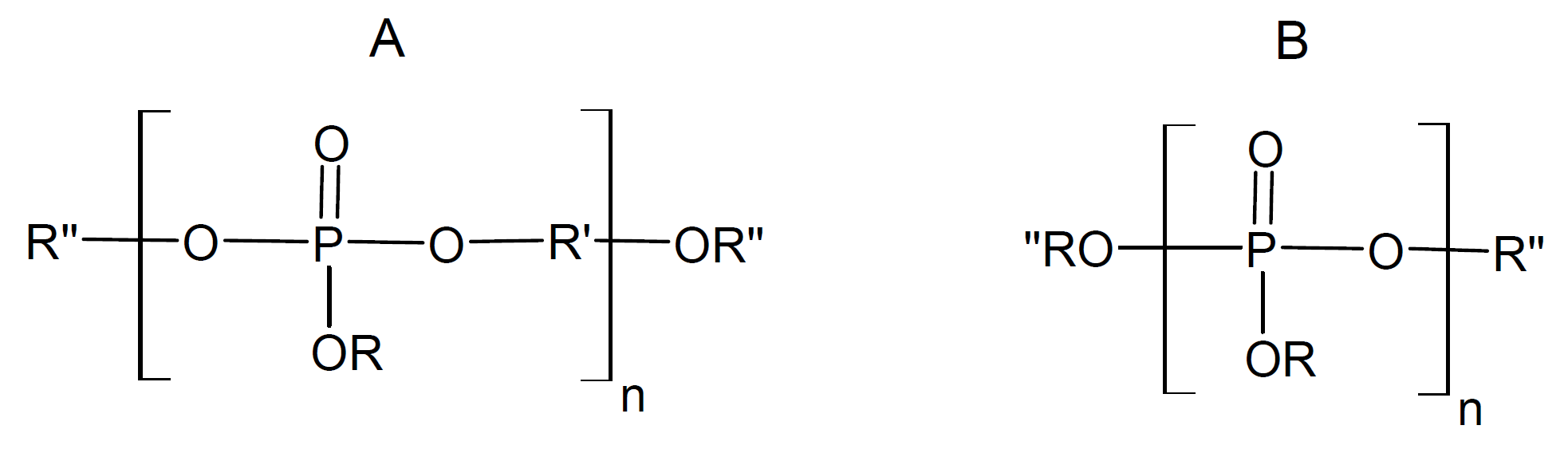
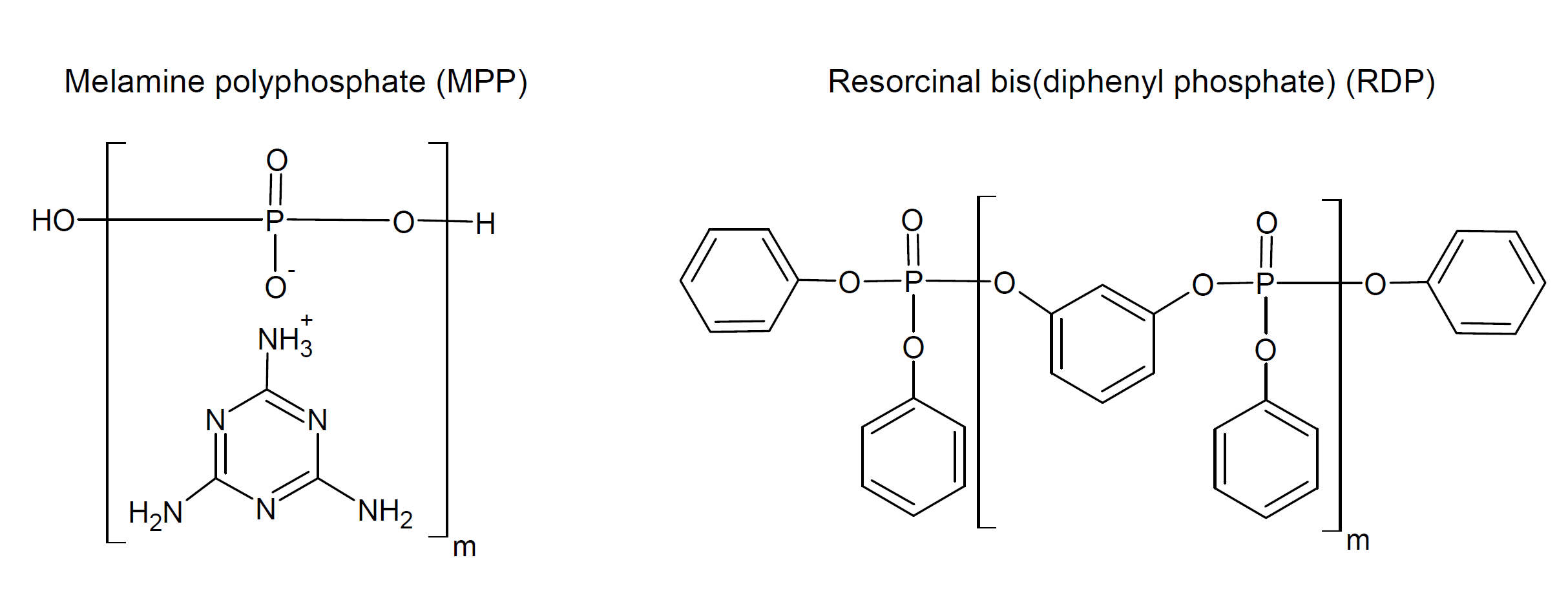
The properties of POPEs can vary signinficantly depending on the side and end groups (R, R''), the organic modification of the backbone (R') (if any), the polymer architecture, and the molecular weight. Typical pendant R and R'' groups include alkyl, haloalkyl, phenyl, melamine or hydrogen, whereas R' can be a residue of bisphenol, hydroquinone, resorcinol or any other dihydroxy organic compound or it can be an orthophosphate repeat unit. Fully inorganic phosphate esters (B: R, R'' = H) are crystalline or amorphous solids which are fully water soluble. They can contain a few to several hundred orthophosphate residues whereas organic polyphosphate esters often contain only a few repeat units (MW ≤ 1000 g/mol) and are either liquid or solid. Some common commercial polyphosphate esters include bisphenol A bis(diphenyl phosphate) (BDP), resorcinal bis(diphenyl phosphate) (RDP), and melamine polyphosphate (MPP)
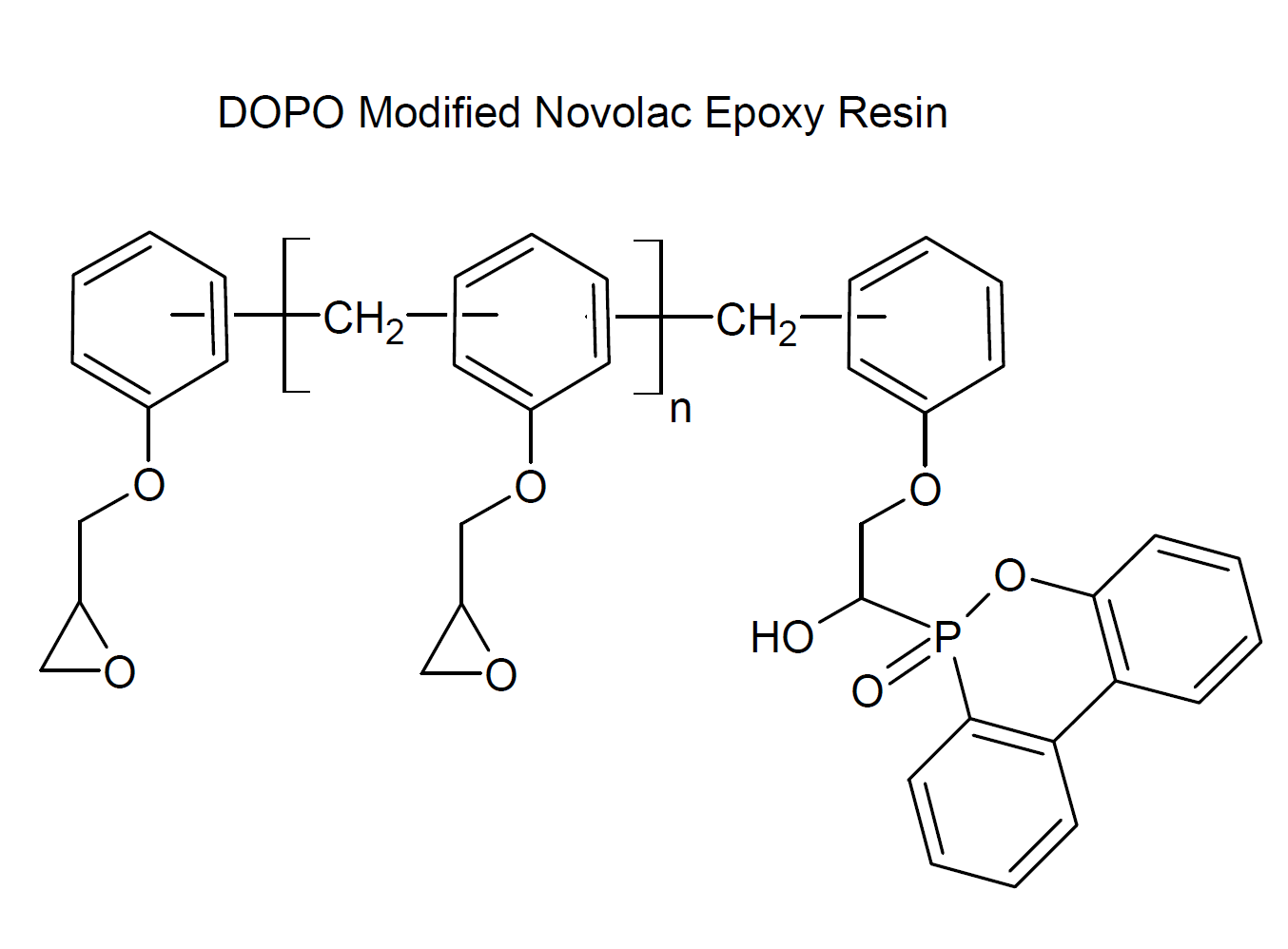
Phosphate esters can also be chemically incorporated in other polymer resins. A common phosphate modified resin is DOPO modified novolac epoxy (DOPO-NE).2 This chemical modification makes the epoxy resin flame retardant.
Another impotant class of phosphate esters are vinyl phosphates such as 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate phosphate (HEMA-Phosphate) and 2-hydroxpropyl methacrylate phosphate (HPMA-Phosphate). These functional monomers, when copolymerized with other vinyl resins, improve adhesion to metals, flame retardancy and corrosion resistance.4
Polyphosphate esters are used for a variety of applications. For example, they can function as flame retardants, water treatment agents, fertilizers5, food additives, refractory bonding agents, adhesion promoters, anti-corrosion agents, plasticizers, hydraulic fluids and high temperature lubricants. Phosphate esters and phosphate modifed resins are also added to paint and coating formulations to reduce their inherent flammability. Biodegradable phosphate copolyesters such as poly(lactide-co-ethyl phosphate) can be used for drug delivery and tissue engineering applications.3
Manufacturers & Distributors
- Hexion (DOPO-NE)
- Shin-A T&C (DOPO-NE)
- ICL (RDP)
- Harcros (Phos. ester)