Phenoplasts (Phenolic Resins)
Properties and Applications
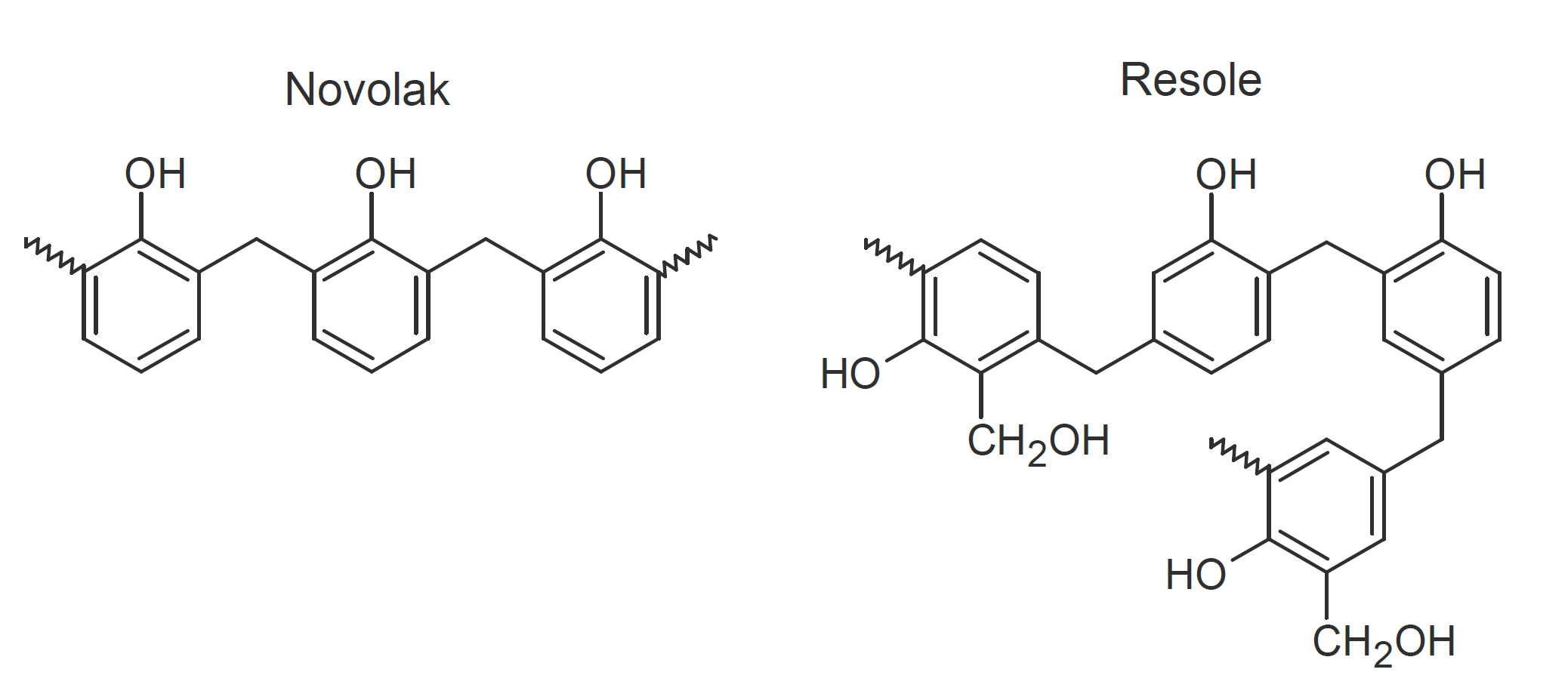
Phenolic resins (also called phenoplasts) are some of the oldest synthetic, high-volume thermosetting resin systems. They are prepared by either acid-catalyzed (novolaks) or base-catalyzed (resoles) addition polymerization of phenol with formaldehyde. Molded parts made of these resins are fine machinable, lightweight and have excellent corrosion and temperature resistance up to 300 - 350°C. They are known for their outstanding dimensional stability, high resistance to creep at elevated temperatures, low humidity absorption, high dielectric strength, and excellent price-to-performance characteristic.
Phenolic resins are used in a variety of products including coatings, composites, adhesives, and molded parts. Due to their low flammability, extremely low generation of toxic gases, and slow heat release, they are often part of structural solutions for the aerospace and transportation industry. For example, glass or carbon fiber reinforced grades are suitable for interior structures of aircrafts. Other important structural applications include components that are exposed to high-temperature and high-pressure environments, for example in industrial and oil and gas applications. Phenolic resins are often an excellent choice for manufacturing protective coatings and for enhancing the performance of other epoxy, acrylic, polyester and alkyd based adhesive and coating products. Important coating applications include tank, drum, can, pipe linings, and marine and industrial coatings. Phenolic resins are also extensively used in the building & construction and furniture industry as binders for wood particleboards.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |