Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Properties and Applications
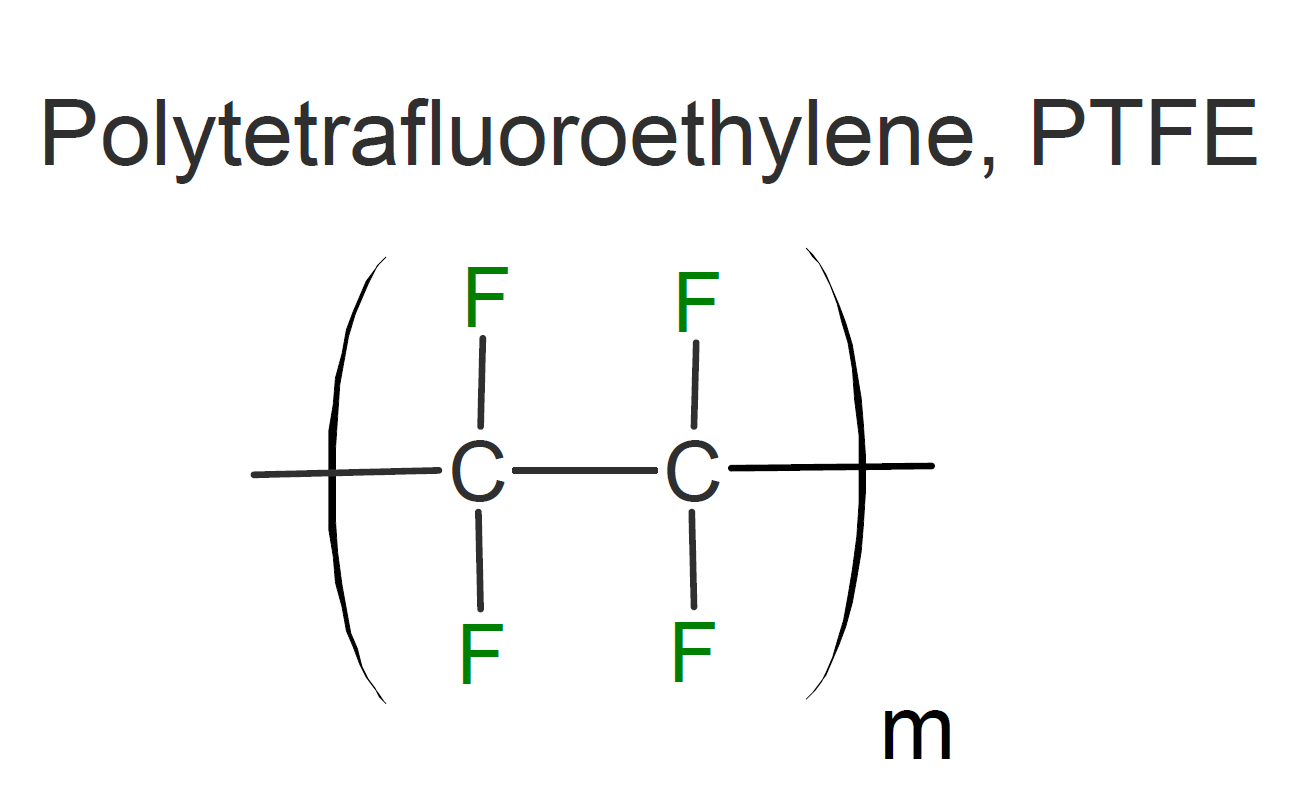
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), more commonly known as Teflon, is the largest-volume fluoropolymer which has a unique combination of properties. For example, it has outstanding thermal, electrical and chemical resistance, is insoluble in all common solvents below its melting point, and its coefficient of friction is among the lowest of all polymers (self-lubricating and non-stick). However, its high crystallinity, very high melting point (600 K), and melt viscosity do not allow its processing by the usual standard melt-processing methods for plastics. Instead, similar to metal and ceramic powders, the granular resins are processed by compression molding at ambient temperature followed by sintering above the crystalline melting point.
PTFE is ideally suited for applications where broad chemical resistance, high durability over a wide service temperature range, excellent dielectric properties and a low coefficient of friction are required or are advantageous. It can be used both at very high (up to 530 K) and extremely low temperatures. However, its high price generally prohibits its use where alternatives exist. Important applications include low-friction bearings, gears and slide plates; chemical resistant valves, pump parts, filters and membranes; non-stick coatings for moulds, dies, and cookware; electrical insulators in connector assemblies, cables and in printed circuit boards.
Companies |
Brands |