Polyphthalamides (PPA)
Properties and Applications
Polyphthalamide (PPA) is a semi-aromatic engineering thermoplastic. The main building blocks are terephthalic acid or isophthalic acid or a combination thereof and at least one aliphatic diamine such as hexamethylene diamine. The aromatic acid portion comprises at least 55 molar percent of the repeat units in the polymer chain, i.e. these resins are only partially aromatic.1-3 The aromatic portion in the polymer backbone increases the melting point, rigidity, heat stability, and chemical resistance and lowers the moisture absorption. However, the enhanced properties come at a price; phthalamide resins are much more expensive than conventional aliphatic amides and are more difficult to process due to their high melting point.
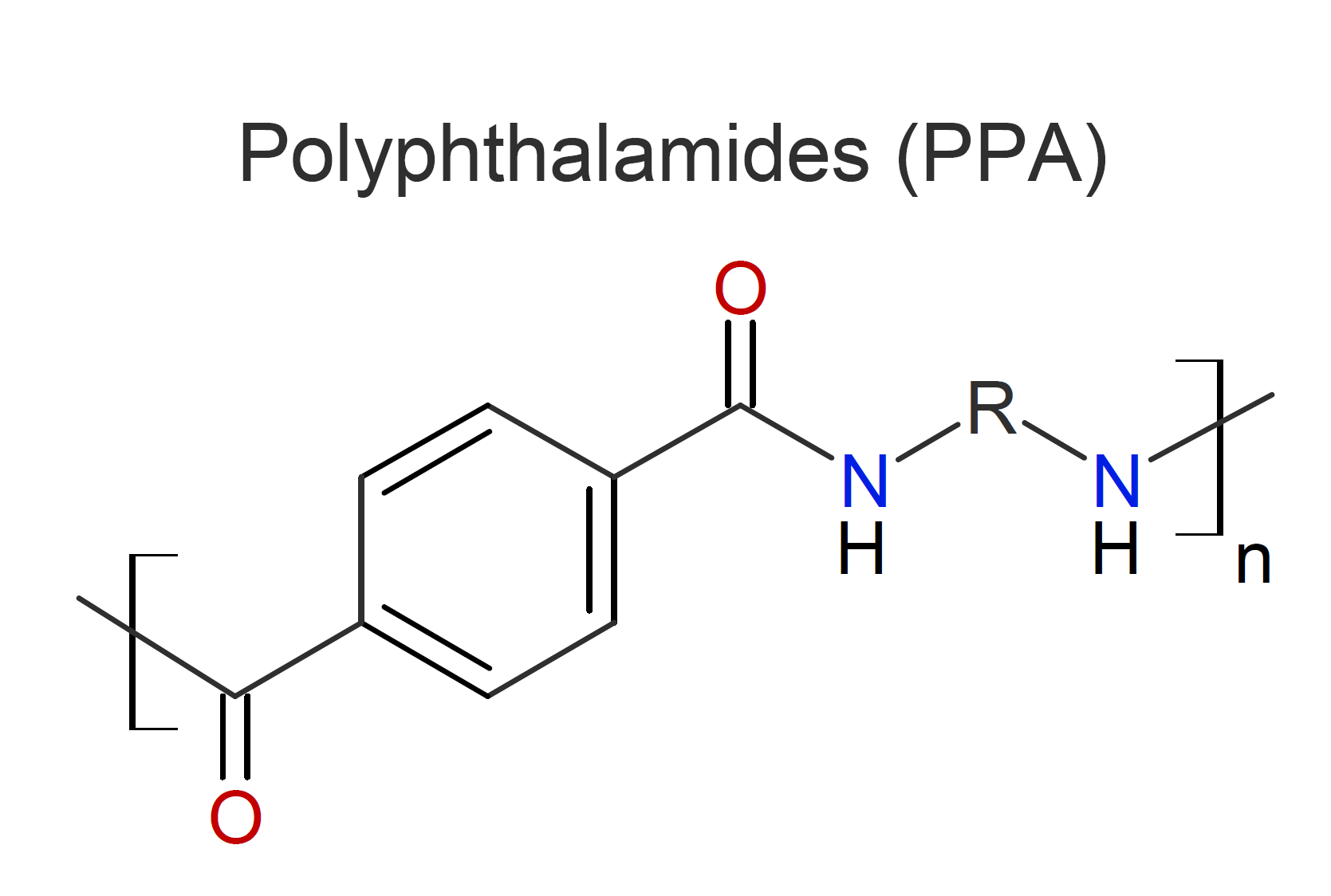
PPA’s are often a cost effective alternative to the more expensive fully aromatic aramids. Common applications include automotive, aerospace, electrical, and industrial parts that must withstand prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals and/or high temperatures. This includes motor parts, fuel line connectors, coolant pumps, bushings, bearing pads in aircraft engines, charge air cooler, fuel cutoff and water heater manifold valves, socket and plug-in connectors, high voltage bushings, motor housings, and head light components.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |