Polyhydroxyethyl Methacrylate (PHEMA)
Properties and Applications
Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) is an important vinyl monomer that can be easily polymerized. The pendant hydroxyl groups make the polymer fully water soluble, whereas lightly crosslinked HEMA forms hydrogels which absorb noticeable amounts of water.1
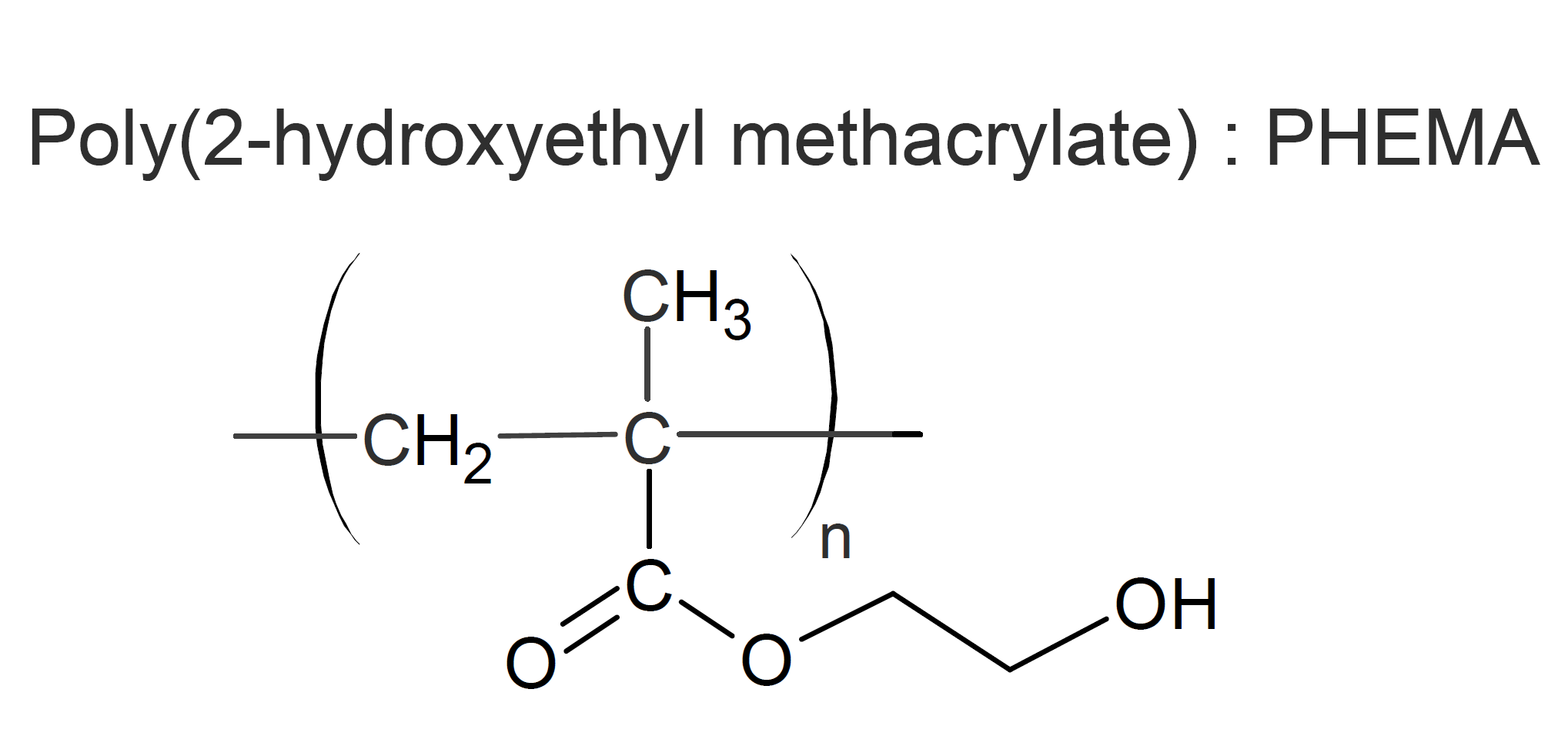
HEMA is frequently copolymerized with other monomers to modify its properties. Due to its low toxicity and hydrophilic character, it has found numerous applications in biomedicine, including contact lenses2, drug delivery systems, and dental adhesives. Another important application of HEMA are isocyanate-free vinyl ester urethane compositions for adhesives, sealants and coatings. The use of HEMA as a capping agent reduces the toxicity of the prepolymers and increases the low shear viscosity efficiency.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Brand Names
1All HEMA-based
hydrogels (contact lenses) are copolymerized and crosslinked with other monomers that make the gel thinner and increase its degree of hydration.
A typical cross-linking additive is triethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (TEGDMA).
2Copolymer hydrogel lenses based on hydroxyethyl methacrylate and ethylene glycol dimethacrylate are sold under the non-proprietary, generic term Polymacon.