Polyethylene Furanoate (PEF)
Properties and Applications
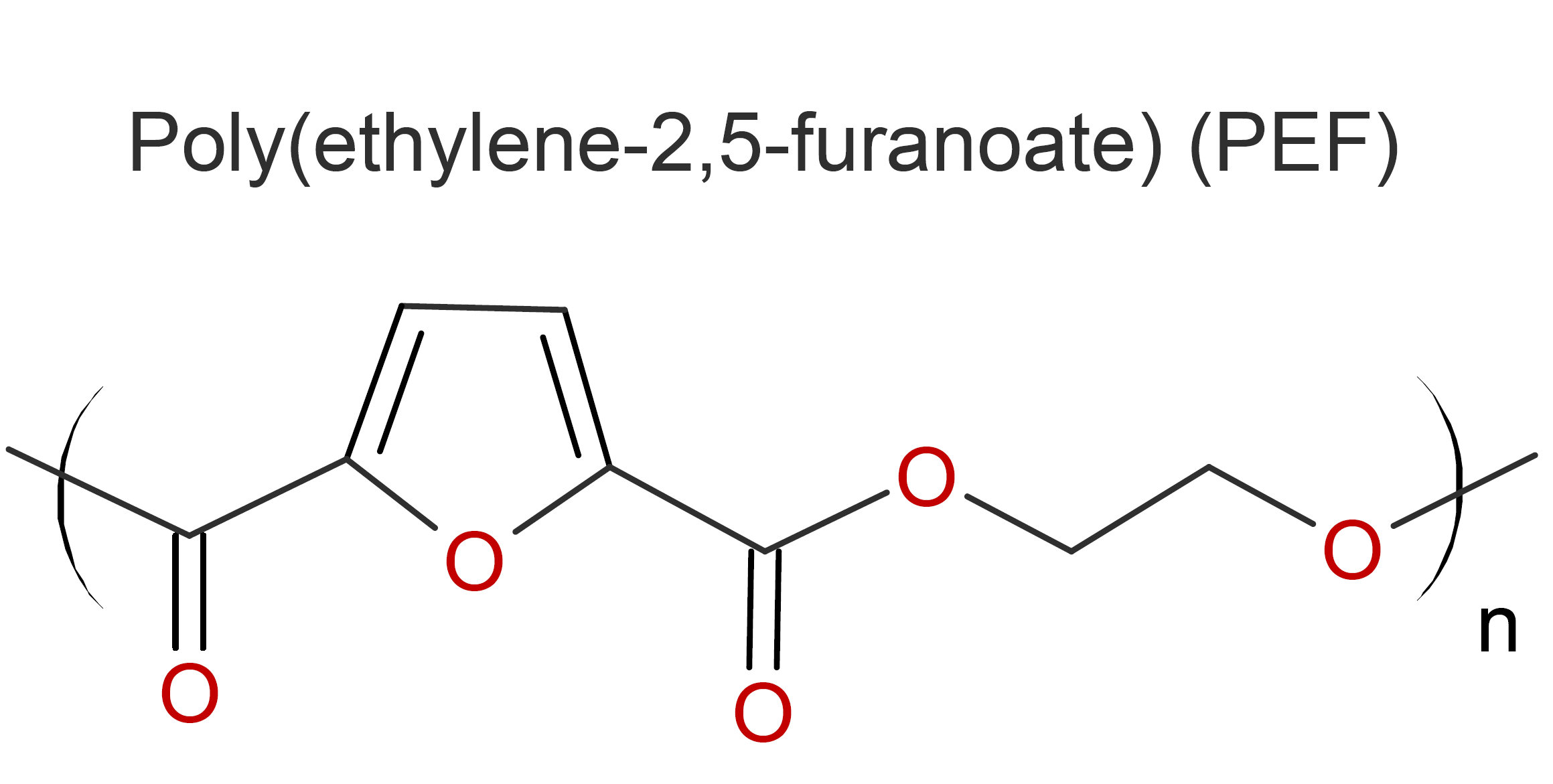
Poly(ethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate) (PEF), also called polyethylene furanoate, is an aromatic, (partially) biobased thermoplastic
polyester that can be easily molded and thermoformed.1 It can be produced by polycondensation of ethylene glycol and 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). The later can be derived from
renewable feedstock (C6 sugar).
PEF has many attractive properties
including high strength and high puncture toughness, good heat resistance,
as well as outstanding gas barrier properties which are superior to PET.2 It also has a lower melting point
and a higher glass transition temperature than PET, and thus has more
attractive thermal and mechanical properties.
PEF is an interesting alternative to polyethylene terephthalte (PET).3 Since it is partially or fully produced from renewable feedstocks, it reduces the carbon footprint. Potential applications include fibers, films as well as food and beverage containers, in particular blow-molded bottles for carbonated soft drinks and alcoholic beverages.
Manufacturers & Distributors4
|
|
1Other biobased furanoates with potential use in packaging applications include poly(isosorbide furanoate) (PIsF), poly(methyl-propylene furanoate)
(PMePF) and poly(1,4-cyclohexane-dimethylene 2,5-furanoate) (PCHDMF)4
2According to Avantium, PEF's gas and vapor permeability is 10 times (O2), 4 times (CO2) and 2 times (H2O) lower than that of PET.
3According to Grand View Research, the global demand for polyethylene furanoate (PEF) is expected to reach almost 17,000 tons by 2022.
4FDCA and PEF is currently (2018) produced on a pilot scale by a joint venture of Avantium, Synvina, and BASF. To ensure optimal product quality, Synvina plans to extend the pilot phase by 24 to 36 months.