Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Properties and Applications
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is the second most important commercial polyester. It is a semi-aromatic thermoplastic that can be easily molded and thermoformed. Depending on the cooling rate and molding process, it is either amorphous or semi-crystalline.1 PBT has many attractive properties like high strength and toughness, good abrasion and heat resistance, low creep at elevated temperatures, good chemical resistance, and excellent dimensional stability, particularly when glass-fiber reinforced.
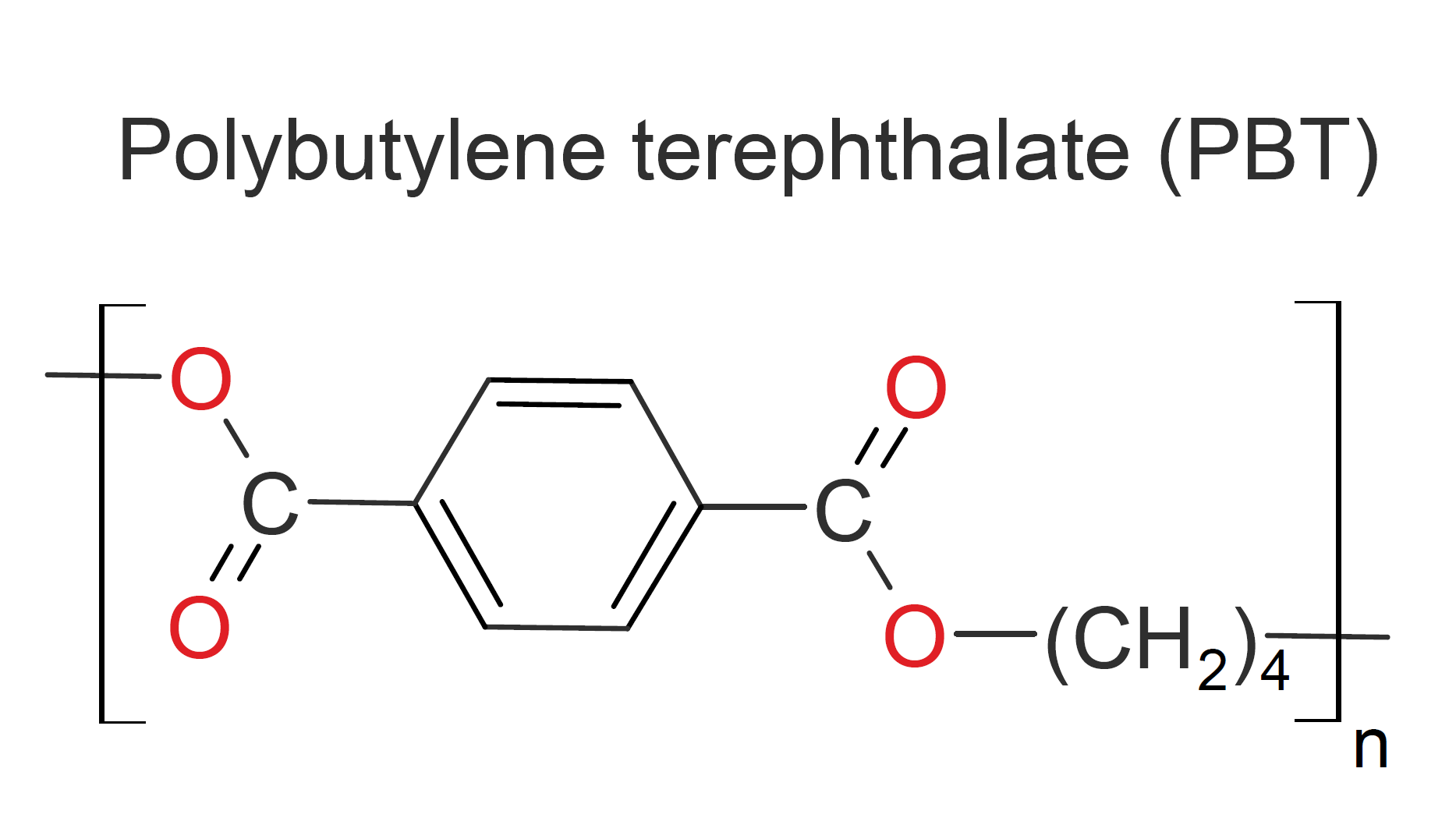
PBT competes with polyethylene terephthalate
(PET) in many engineering plastics applications. Compared to PET, it has
somewhat lower strength and rigidity but is more flexible and tougher
(higher impact strength). It also has a slightly
lower melting point and crystallizes much faster than PET. Its maximum use temperature is
typically between 115 - 135°C
(240 - 275°F) which is slightly lower than that of PET.
Like
PET, PBT finds many uses as an engineering thermoplastic, particularly in electrical and automotive applications, including plug connectors, relays, keyboards, switches, distribution boxes, and fiber optic cable jackets.
Manufacturers |
Brand Names |