Polybutylene Succinate (PBS)
Properties and Applications
Poly(1,4-butylene succinate) (PBS) is a biodegradable, semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester synthesized through polycondensation of succinic acid and 1-4-butanediol. Both building blocks can be produced either from renewable feedstock such as glucose and sucrose via fermentation or from petroleum-based feesstock.1
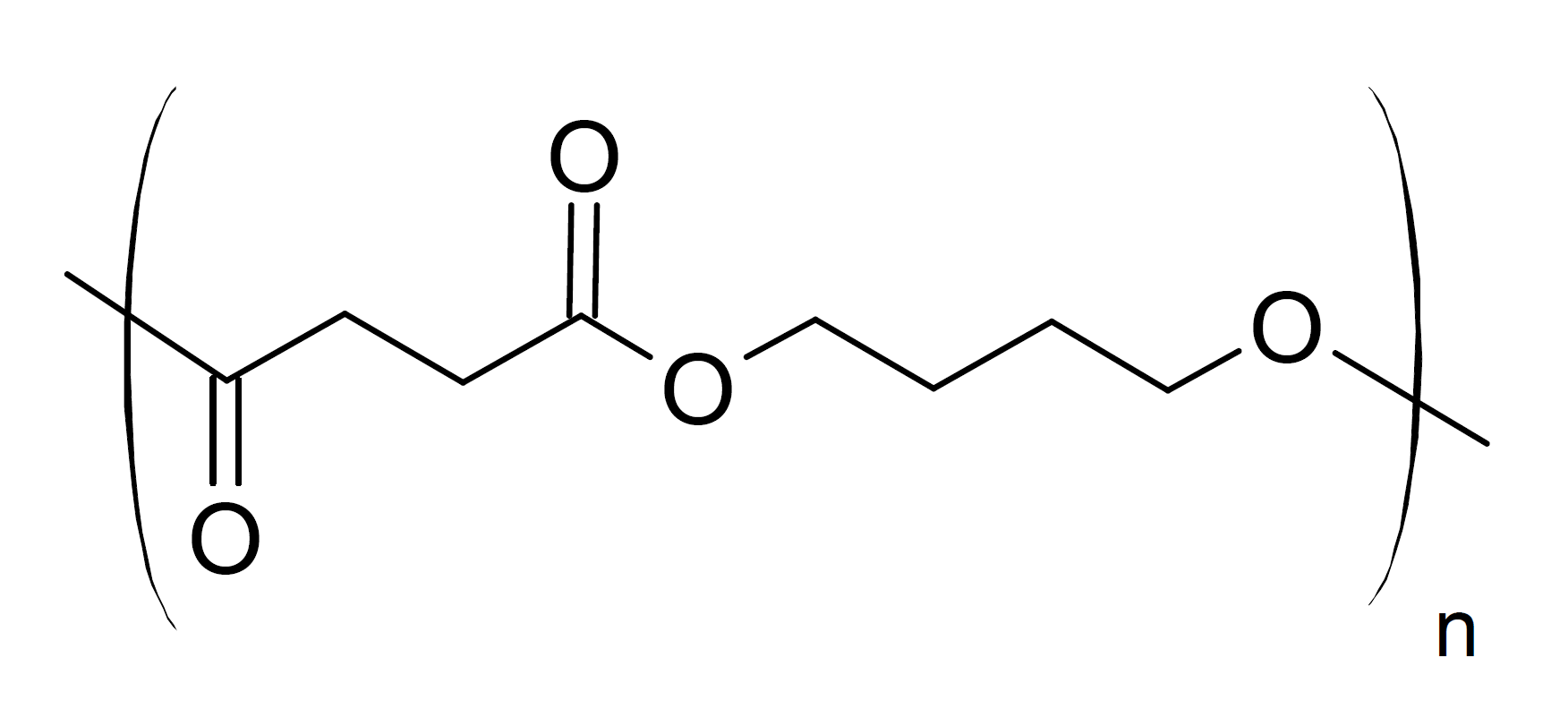
PBS is a very promising biopolymer because its mechanical properties are comparable with those of widely used high density polyethylene and isotactic polypropylene. Like polylactic acid (PLA), it fully decomposes into biomass, CO2 and H2O and thus can be disposed off together with other organic waste. However, it is much more flexible and thus does not require plasticizers, but has a lower melting point than PLA (115°C vs ~160°C).
PBS is one of the newest biopolymers and could be a cost-effective alternative to other biopolymers such as PLA, PBAT, and PHB. It can be used either as a matrix polymer or in combination with other bioolymers such as polylactic acid (PLA). Possible applications include food packaging, mulch film, plant pots, hygiene products, fishing nets and fishing lines.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1In 2016, the italian biochemical company Novamont and its California based partner Genomatica opened the world’s first industrial scale plant for the production butanediol via fermentation of renewable raw materials. The new plant will produce 30,000 tonnes/year of low-impact biobased-butanediol, with savings of more than 50% in terms of CO2 emissions. Source: Novamont News & Media, September 2016
2Succinity is a joint venture of BASF and Corbion.