Polyamide 4/6 (Nylon 4/6)
Properties and Applications
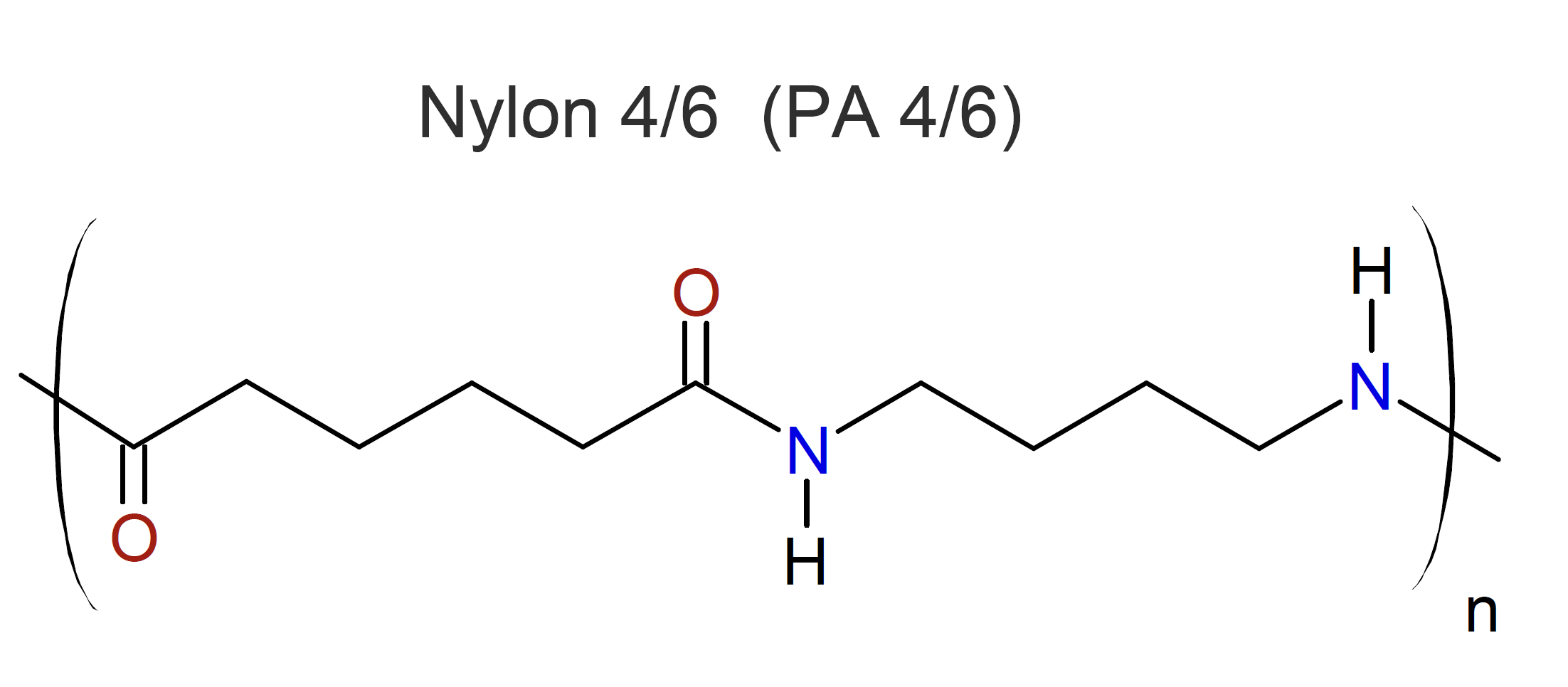
Polyamide 4/6 (also called Nylon 4/6) is a semi-crystalline, yellowish engineering thermoplastic made by condensation polymerization of 1,4-diaminobutane with adipic acid. Compared to many other aliphatic nylons, it has a higher melting point of 295°C, a higher crystallinity, a faster rate of crystallization and much better retention of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures.1,2 The superior high temperature properties can be explained by the larger number of amide groups per given chain length and by the more symmetrical structure which facilitates crystallization.
Like other engineering polyamides, Nylon 4/6 has excellent wear resistance, good electrical insulation properties and high chemical resistance to many chemicals including fuels, greases and oils at elevated temperatures. However, its moisture absorption is higher than those of standard polyamides 6 and 6/6 due to the more polar backbone. It is also more sensitive to stress cracking due to the higher crystallinity. On the upside, it has a much higher heat deflection temperature (HTP), tensile strength, and heat resistance.
Nylon 4/6 is available in various grades, including unreinforced and reinforced with glass fibers. It is used in many industries where high mechanical strength and ductility, good dimensional stability, and high heat and chemical resistance is required or recommended. Important applications include electrical connectors and electrical components, gears, bobbins, fasteners, bearings, bushings, guides, crank shaft saddles, pump parts, and actuators. In many cases, it can replace metals, thermosets and more expensive thermoplastics such as PEI, PES and PPS.
Manufacturers |
Brand Names |