Orthosilicates
Properties and Applications
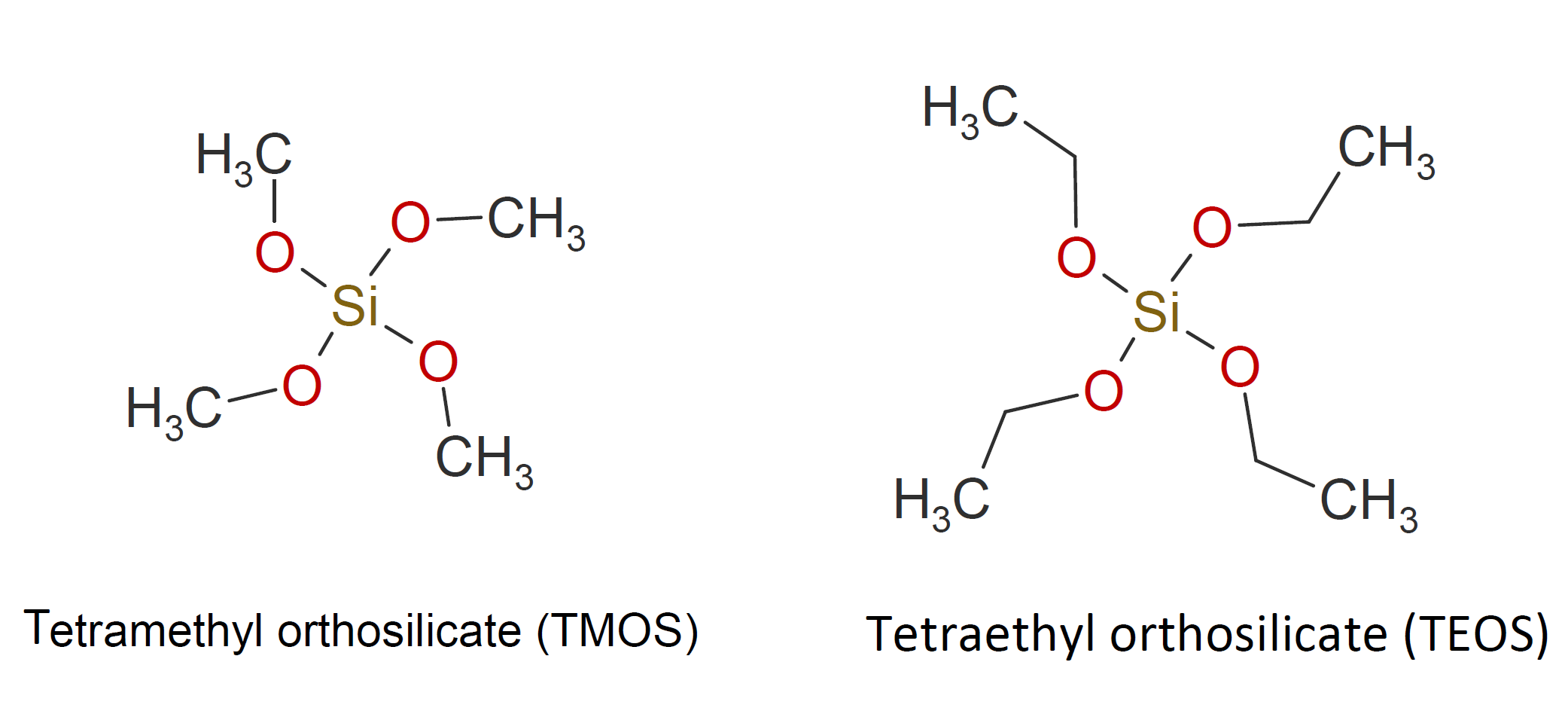
Orthosilicates are any salt or ester of orthosilicic acid, (M+)4SiO4- or Si(OR)4. Two very common orthosilicates are tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and tetramethyl orthosilicate (TMOS). Both silicates are colorless, transparent liquids that are widely used as inorganic crosslinking agents or binders. TEOS is usually preferred over TMOS, because TMOS releases toxic methanol when hydrolyzed whereas TEOS releases ethanol.
Orthosilicates are frequently used as binders in zinc-rich coatings for corrosion protection of steel. When exposed to moisture in the atmosphere, the orthosilcates hydrolyze in the presence of acid or base catalysts and subsequently condense to an inorganic polysilicic acid network. Orthosilicates such as TEOS find also uses as a semiconductor silicon source. They can be used as a replacement for silane and other silicon sources for thin film deposition (chemical vapor deposition, CVD) of doped and undoped silicon dioxide. TEOS is also used as the silica source for the synthesis of some zeolites.
Orthosilicates are sometimes blended with silane and silicon compounds to prepare sol-gel hybrid organic-inorganic coating products. These so called organically modified silicates (also called ormosils or sol-gel coatings) have improved mechanical properties and are employed for a multitude of applications in the electronic, building, industrial and medical industries.