Nafion - Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid
Properties and Applications
Nafion was first developed by Walter Grot at DuPont in 1964.1 It is a perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) polymer which is produced by free-radical copolymerization of tetrafluoroethylene (the monomer of Teflon) with a perfluorinated vinyl ether comonomer. Nafion contains a small proportion of sulfonic acids groups which make this polymer highly ion-conductive (ionomer). Like Teflon, it has outstanding heat and chemical resistance. According to DuPont, only molten alkali metals (sodium in particular) and elemental fluorine can attack Nafion.1
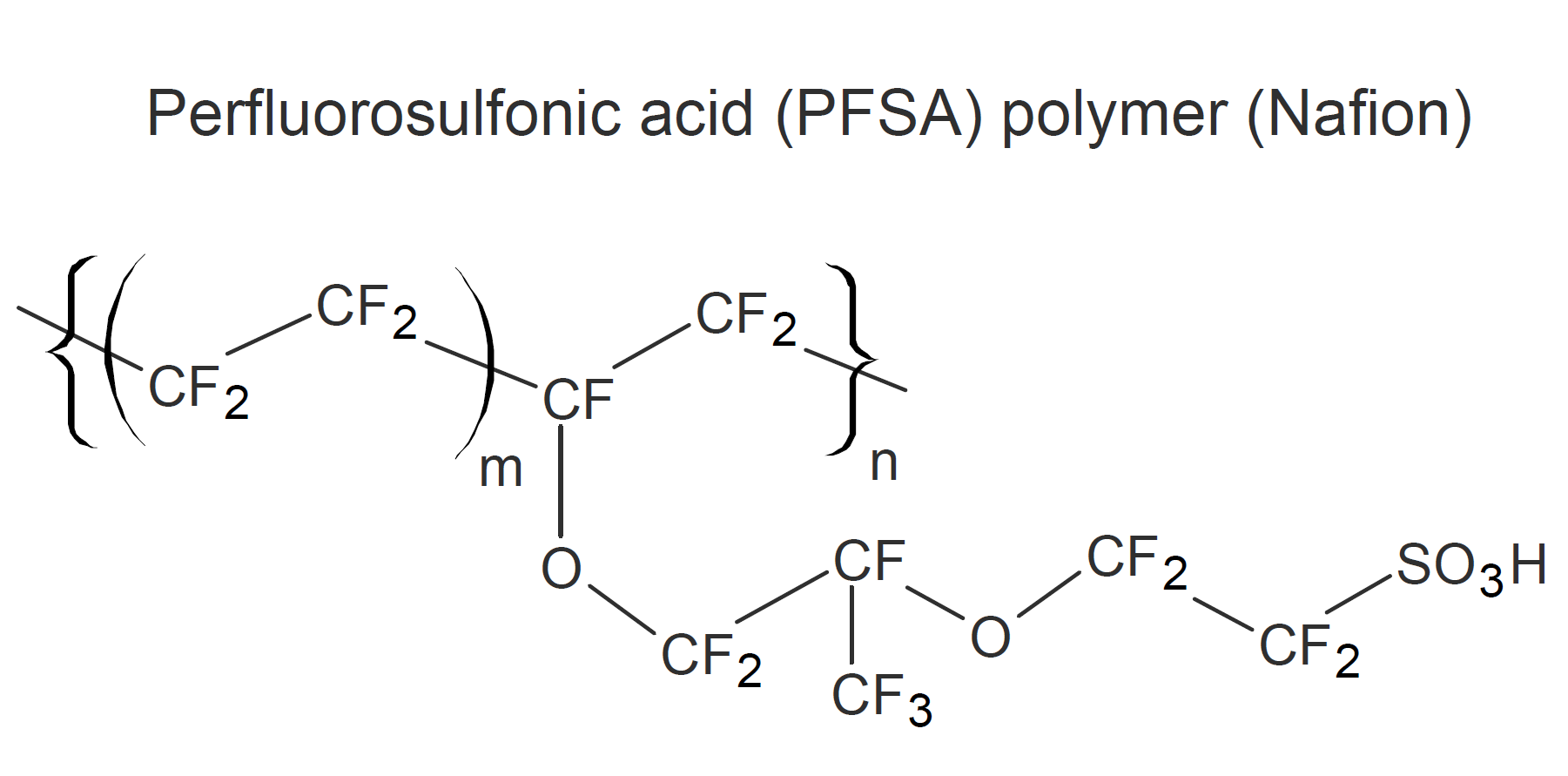
Perfluorinated sulfonic acid ionomers are often used as ion-selective membranes. Important applications include cation exchange membranes for fuel cells, PEM water electroyzers, separators for redox flow batteries, electrodialysis, and electrochemical hydrogen compressors. In some applications, Nafion membranes can be operated at temperatures as high as 190°C.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1Walter G. Grot, Nafion Membrane and its Applications. In: U. Landau, E. Yeager, and D. Kortan(1982), Electrochemistry in Industry, pp 73-87, Boston, MA 1982