Fluoroethylene Vinyl Ether (FEVE)
Properties and Applications
FEVE resins are copolymers of a fluoroethylene monomer (FE) and a vinyl ether monomer (VE). These resins were developed to overcome the processing disadvantages of traditional fluoropolymer resins which have to be melted or solubilized at relative high temperatures to form a barrier coating.1 The chemical structure of the FEVE polymer is shown below.
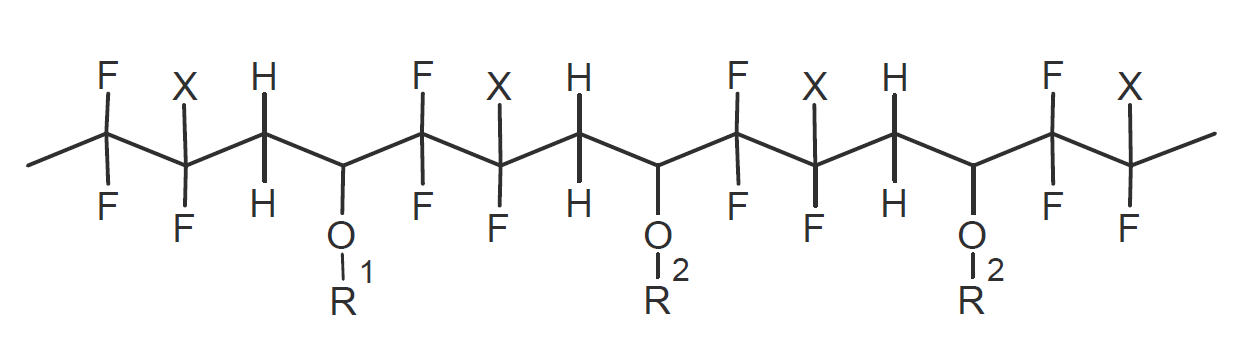
Like other fluoropolymers, FEVE has excellent chemical and UV resistance which increases with the number of fluorine atoms in the repeat unit. Increasing the fluorine content also lowers the coefficient of friction and raises the melting point whereas a higher vinyl ether content improves solubility in many solvents. The vinyl ether groups also contribute to high gloss and allow for reactive sides or functional groups to be incorporated into the polymer.
The main application of fluoroethylene vinyl ether resins are architectural coatings. The incorporation of these resins provides excellent gloss and color retention. FEVE resins are also known to improve corrosion and weathering resistance, especially in marine environments where coatings are exposed to both strong UV radiation and high levels of corrosives. However, FEVE resins are rather expensive and therefore only added to coatings when superior weathering resistance and durability is required.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Companies |
Brands |
1W. Darden, T. Takayanagi and S. Masuda, NACE International, NACE-07009 (2007)