Epoxy Vinyl ester Resins
(Novolac and DGEBA Vinyl Ester Resins)
Properties and Applications
Epoxy vinyl esters are an important class of thermoset molding resins. They are the condensation product of vinyl acids and epoxy resins. The two main types of epoxy resins are Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA) and epoxy phenol novolac (EPN) and common acids include acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, terephthalic acid, and fumaric acid. Other unsaturated or vinyl co-reactants include maleic anhydride, phthalic anhydride, dimer fatty acid, and glycidyl methacylate. Novolac based vinyl esters are sometimes chosen to achieve better thermal and chemical resistance, whereas dimer fatty acid - glycidyl methacylate modified vinyl resins have improved flexibility but reduced chemical and heat resistance.
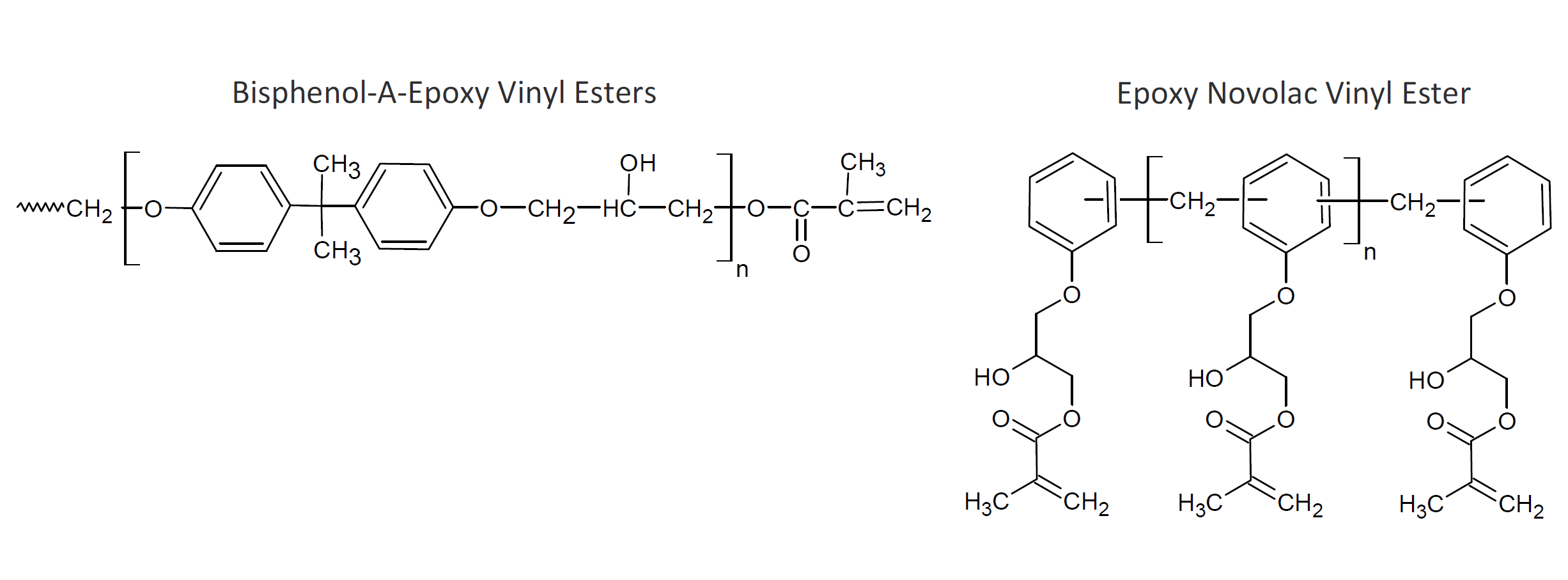
The vinyl esters are typically diluted with styrene to a solid content of about 30 to 40% and cured with a conventional organic peroxide. The copolymerization with vinyl monomer improves the overall chemical and corrosion resistance. Such resins form durable laminates and coatings when fully cured. Their performance is often between those of conventional polyesters and epoxy resins.
Epoxy vinyl ester resins have superior resistance to corrosive chemicals and environments than common unsaturated polyesters such as BPA vinyl esters. For this reason, they are extensively used in the production of corrosion resistant coatings, linings, and molded composites, which find applications in the chemical and marine industries to create a superior barrier for (salt) water and chemicals.