Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Terpolymer
(Ethylene vinyl acetate Maleic Anhydride)
Properties and Applications
Ethylene vinyl acetate terpolymers (EVA-MAH) are random copolymers of ethylene, vinyl acetate and maleic anhydride produced by high-pressure polymerization in tubular reactors.1 The ethylene portion provides miscibility with ethylene copolymers while the vinyl acetate portion increases the softness, flexibility and polarity and the maleic anhydride functionality in the polymer backbone provides reactivity and crosslinking ability when blended with resins having amine (-NH2), isocyanate (NCO) or hydroxyl groups (-OH). These copolymers are compatible with many polymer resins and additives including polyamides, polyurethanes, LDPE, tackifying resins and waxes. They possess high clarity and are sufficiently thermal stabie to be blended and processed by extrusion. When blended with other resins, they improve dispersion during melt mixing, green strength, and adhesion performance.
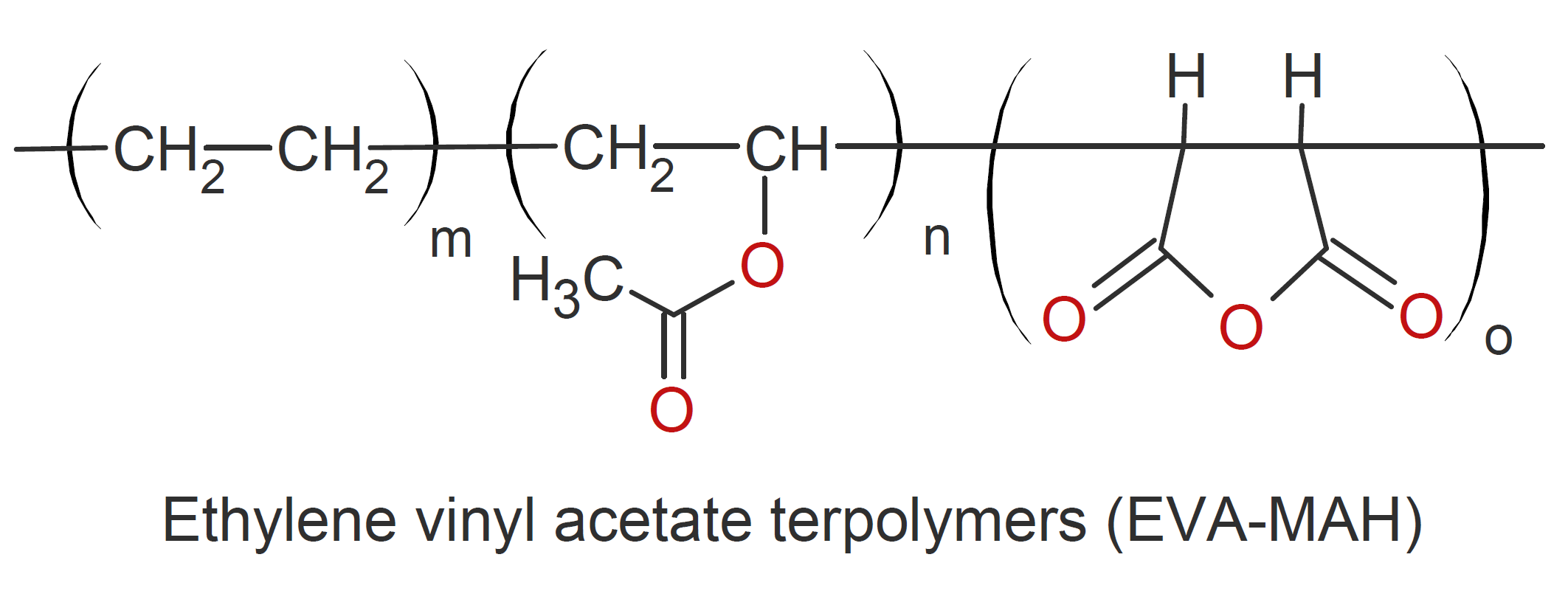
EVA-MAH are important adhesive resins that bind to both polar and non-polar substrates. They can be used as tie layers between polyethylene and polyamide in blown films or in thermo-adhesive films to bond various substrates including PA, PET, PU films as well as metal foils, textiles and (PU) foam products.3 When used as thermo-adhesive films, they are often applied in a second step, under pressure and heat activation, by a blow molding or cast film process.
Important end-use applications include assembly of door panels, seats and roofing in the automotive industry; assembly of sports and leisure goods such as skis, sails, shoes; and bonding of decorative films, mattresses, seats, and wall coverings in the furniture industry. Other applications include hot melt adhesives, pipe coatings (shrink sleeves and tapes) and co-extruded tubes with polyamide as inner layer and polyethylene or EVA as external layer.4
Manufacturers |
Brand Names |