Polydicyclopentadiene (DCPD)
Properties and Applications
Polydicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a
highly reactive thermoplastic resin
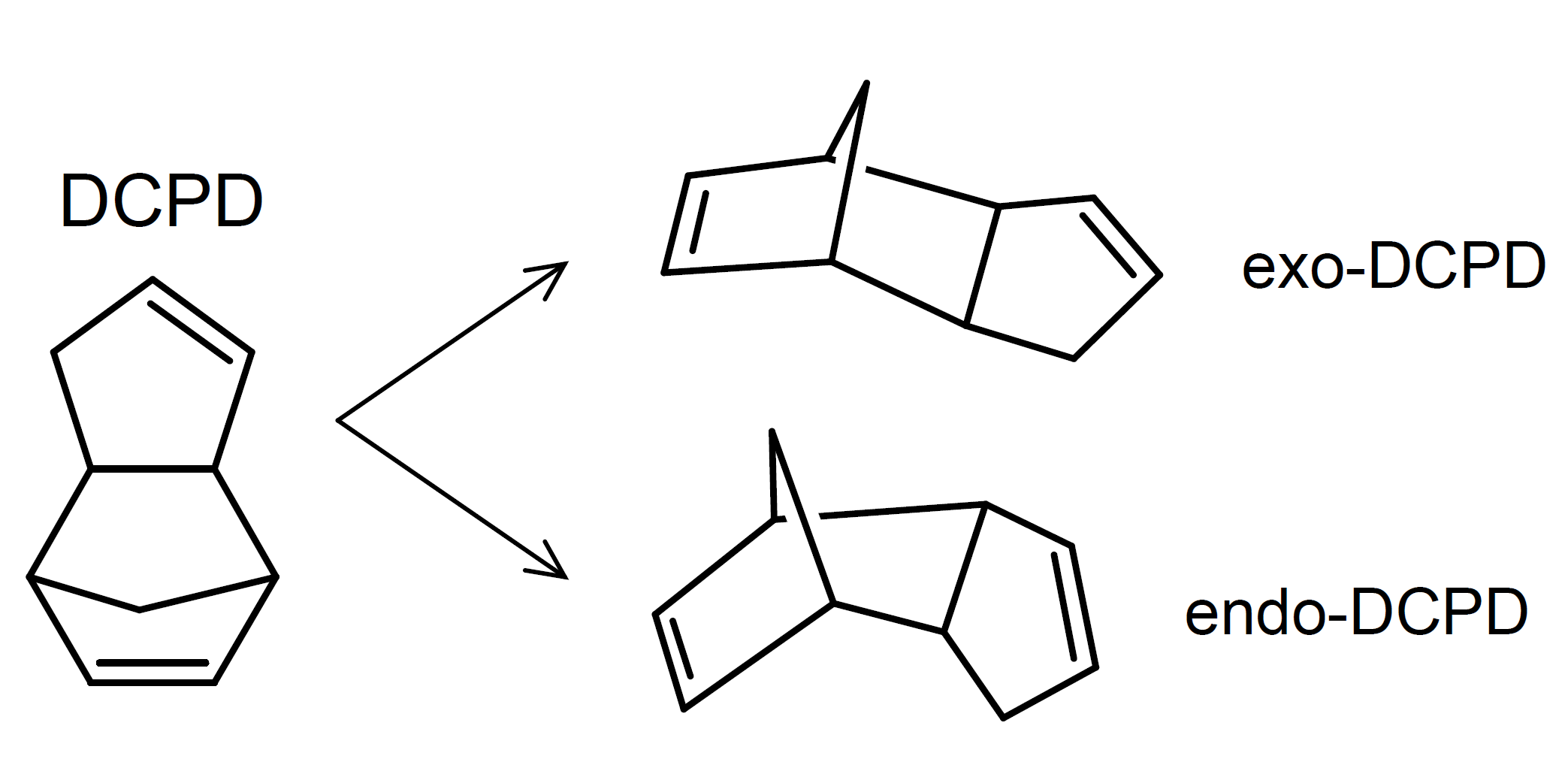
formed by a Diels-Alder addition reaction of two cyclopentadiene molecules yielding two stereo-isomers:
endo-DCPD and exo-DCPD.1
DCPD
readily copolymerizes with many vinyl monomers and resins including alkyds, unsaturated esters, phenolics and epoxies.
It functions as a reactive diluent, cross-linking agent and curative.
One of the most important applications is the production of unsaturated polyester resins which can be reaction transfer molded (RTM) or reaction injection molded (RIM) into large parts. DCPD improves the processability (higher filler loading) and surface quality of sheet and bulk molded parts consisting of fiberglass/fillers, and unsaturated polyester. It also provides excellent dimensional stability (higher HDT and lower shrinkage), as well as improved toughness, stiffness and corrosion resistance which are typically better than those of traditional unsaturated polyester resins. Another prominent application is EPDM rubber (ethylene propylene diene monomer); when copolymerized with olefins, it provides cross-linking sites for vulcanization. DCPD is also used for high quality optical lenses and in formulated products such as hot melt adhesives (tackifier resins), varnishes, and paints.