Diallyl Phthalates (DAP, DAIP)
Properties and Applications
Diallyl phthalate (DAP) and diallyl iso-phthalate (DAIP) are thermosetting ester resins produced by the reaction of allyl alcohol with ortho-phthalic anhydride and meta-phthalic anhydride, respectively. The cured resins have excellent electrical insulating properties including high insulation resistance and low electrical losses, even when subjected to to high heat and humidity over long periods of time. They also have excellent dimensional stability and do not warp in high-heat applications. Furthermore, they have low moisture absorption, excellent weathering properties, and good chemical resistance to many chemicals and solvents including aliphatic hydrocarbons, oils, alcohols, acids, and alkalis.
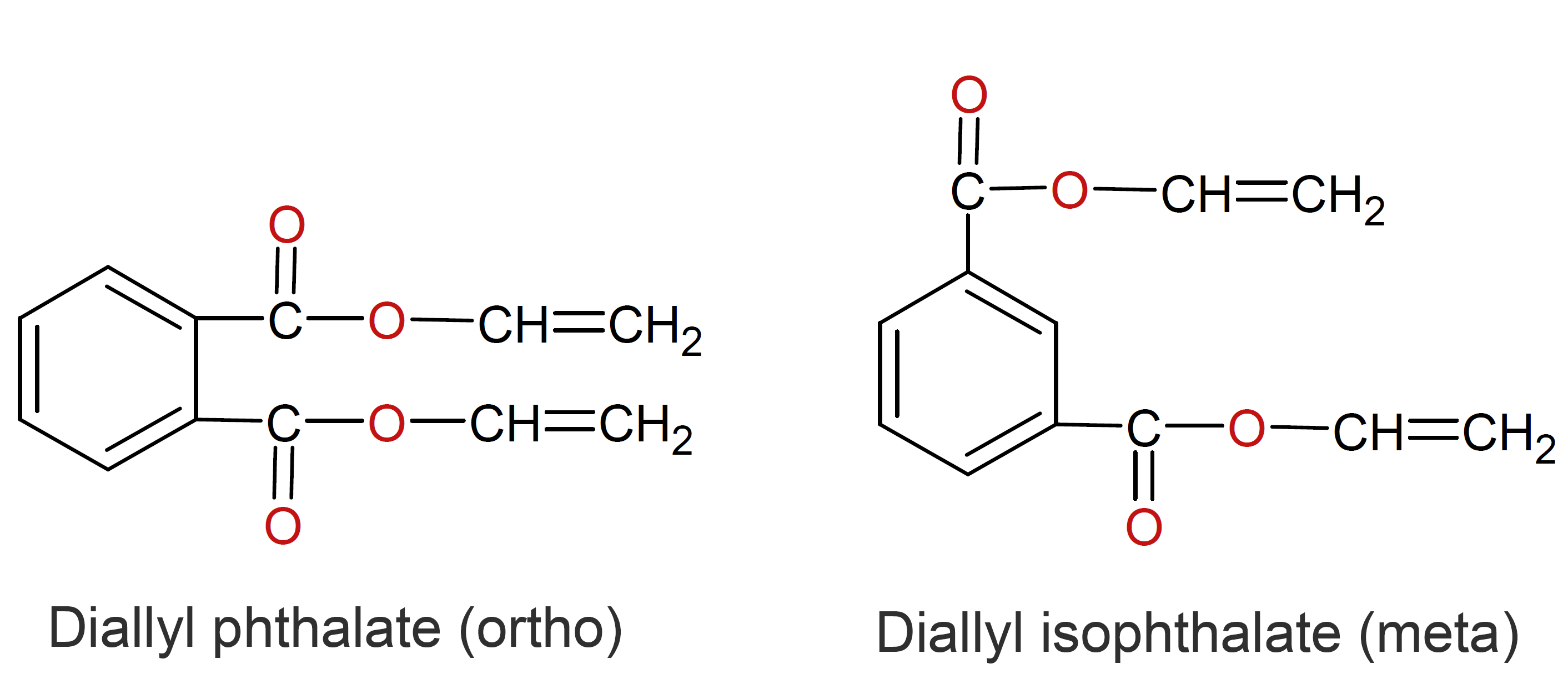
The monomers are often used as cross-linking agents in unsaturated (alkyd) polyester resins. As polymers, DAP and DAIP prepolymers are mainly used as molding resins for electrical and electronic parts such as switches, connectors, control panels, circuit breakers, terminal boards, resistors, and insulators. Other (potential) applications include laminates, prepregs, headlight lamp reflectors, bathtubs, sinks, appliance handles and control knobs.