Polycyanoacrylates
Properties and Applications
Cyanoacrylates are commercially important, highly reactive monomers that are mainly used for rapid-curing adhesives. To facilitate easy handling, they are frequently formulated with thickeners such as fumed silica to make them more viscous or gel-like. Cyanoacrylates rapidly polymerize in the presence of water, to be more specific in the presence of (trace amounts) of hydroxide ions. For this reason, any slightly alkaline surface with trace amounts of adsorbed water will cure by first neutralizing the acidic stabilizers in the adhesive and then initializing rapid polymerization, whereas acidic surfaces may delay or even prevent curing.
The most widely used cyanoacrylates include methyl 2-cyanoacrylate, ethyl-2-cyanoacrylate, n-butyl cyanoacrylate, and octyl-2-cyanoacrylate. The later was introduced to address (minor) toxicity concerns and to reduce skin irritation and allergic response when used in the medical field.
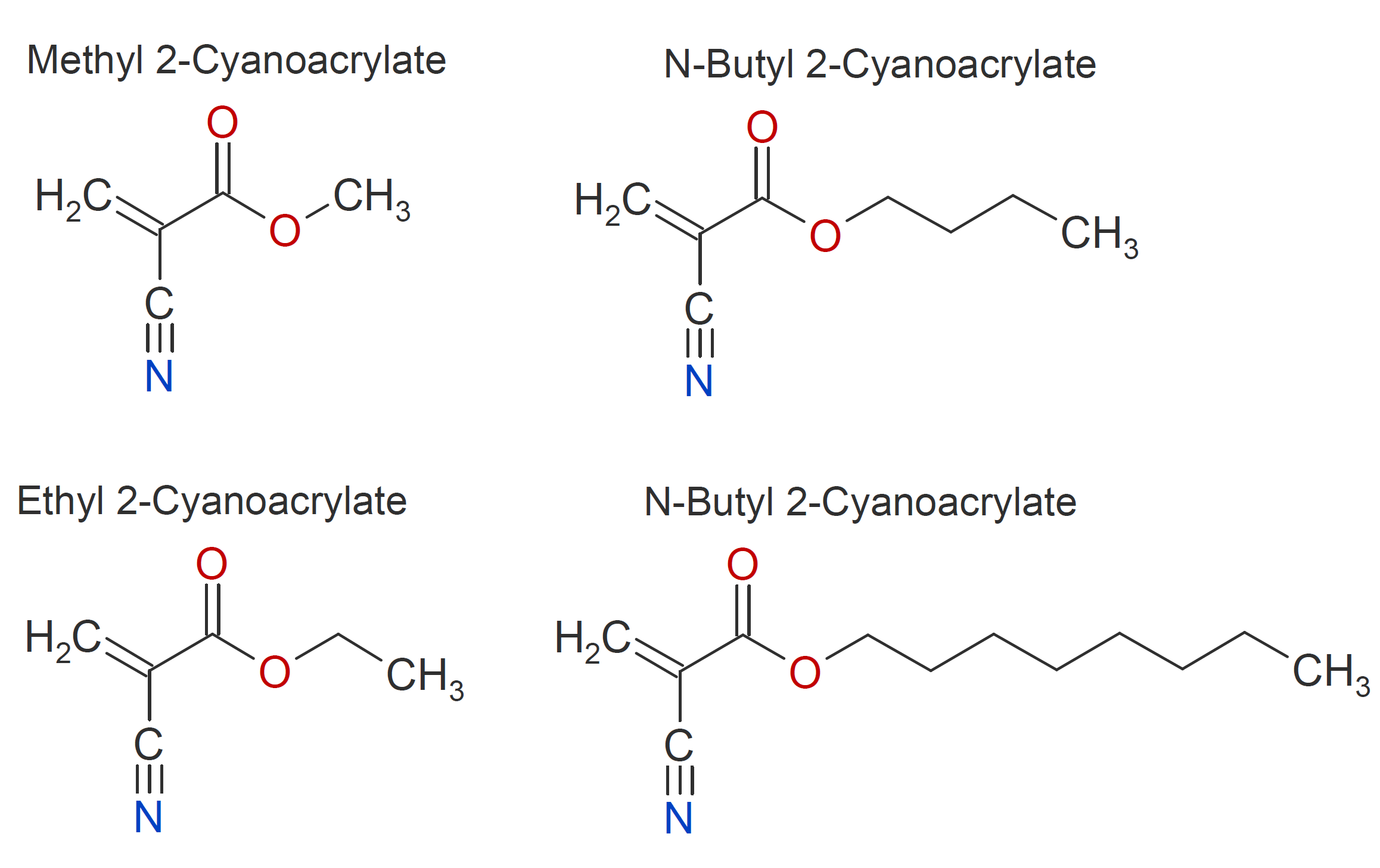
Cyanoacrylates are mainly used as fast-curing structural adhesives with industrial, medical, and household uses. They bond many different substrates including metal, plastic and glass. However, unlike many other adhesives, they do not fill spaces. In fact, a very thin layer bonds more effectively than a thicker one. Their effectiveness in bonding metal and their general versatility have made cyanoacrylates very popular adhesives.
Manufacturers & Distributors
|
|