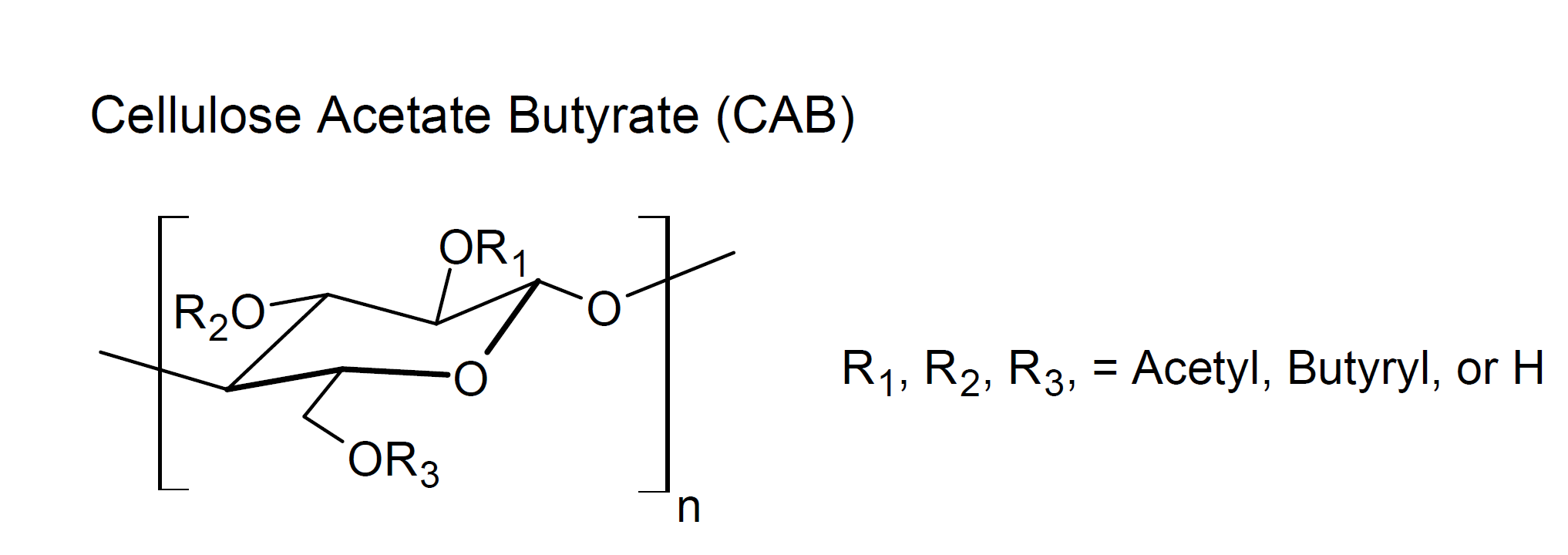
Cellulose Acetate Butyrate (CAB)
Properties and Applications
Cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB) is a thermoplastic cellulose ester with 30 to 55 wt% butyryl content. It is the most commercially important mixed cellulose ester and has many attractive properties such as low viscosity, high transparency and surface gloss, improved resistance to moisture and ultraviolet light (UV), and good inter-coat adhesion. CABs are compatbile with many resin systems, including most acrylics, polyesters, phenolics, ureas and isocyanates. However, they are often incombatible with melamine, urea-formaldehyde and many alkyds. Both the solubility and miscibility depends on the butyryl content; in general, with increasing butyryl content, the solubility in many resins and solvent increases. For example, CAB resins with high butyryl content are soluble in many esters, ketones, glycol ethers, blends of alcohols, and aromatic hydrocarbons.1
CAB is often used in coating formulations where low application viscosities at relatively high solid content are required. When added to coating formulations, it improves many coating properties like hardness, leveling, solvent resistance, clarity and gloss while it reduces dry-to-touch time, cratering, orange-peel and blocking. Due to CABs superior properties, it finds many uses in coatings including metal and wood coatings, gravure and flexographic printing inks, graphic arts, ink jet printing inks, nail lacquer topcoats, automotive clear and base coats, and general industrial coatings.
Manufacturers & Distributors
1Source: Eastman™ 'Cellulose-based Specialty Polymers' brochure, E-325H 10/14