Polybenzoxazines
Properties and Applications
Polybenzoxazines are a new class of high-performance thermoset resins that resemble conventional phenolic resins but overcome many of their weaknesses. They are formed by reacting a phenol or bisphenol-A with formaldehyde and an aromatic amine and cured by thermal ring-opening polymerization, leading to double-chain or double-strand polymer:
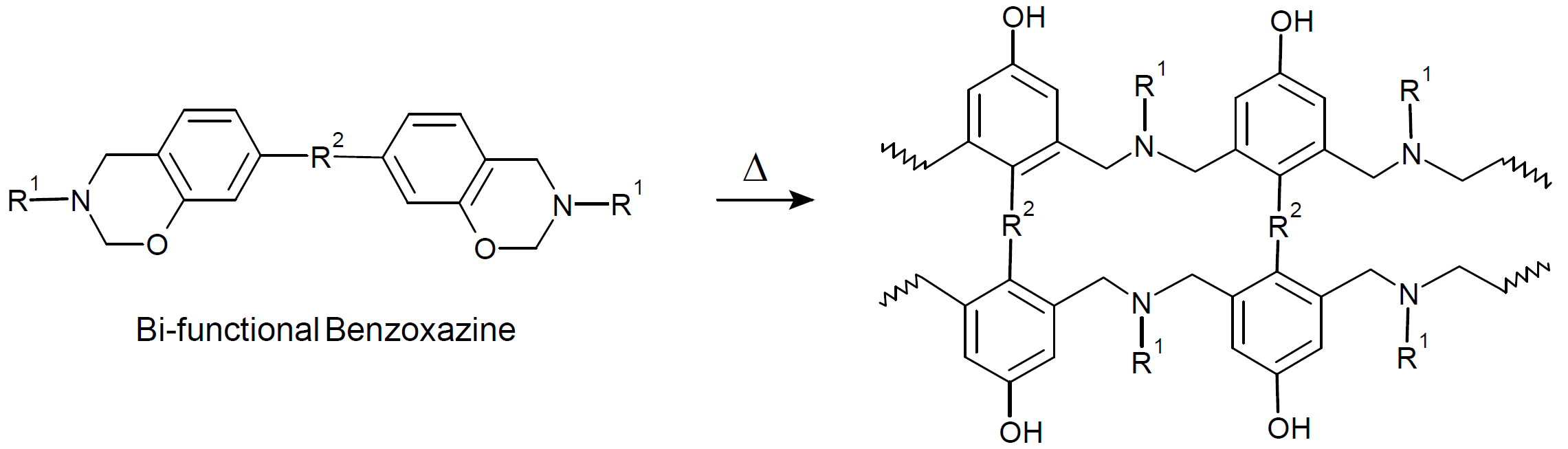
Typical benzoxazines have a high glass transition (140 - 250°C) and high decomposition temperature and are, therefore, well suited for high temperature applications. Other useful properties include low water absorption, very little cure shrinkage, low dielectric properties, high flame retardance, and outstanding thermal mechanical properties. They are typically stiffer, have better chemical resistance, and less cure shrinkage than bismaleimides, epoxies and phenolics.1 They also have very high flame retardancy superior to PEI, phenolics and PEEK. However, (unmodified) polybenzoxazines also exhibit some deficiencies including high curing temperature and low fracture toughness. These weaknesses can be overcome by blending benzoxazines with toughening agents and other resins.2
Polybenzoxazines have many (potential) applications such as halogen-free laminates for printed circuit boards; chemical and heat resistant coatings, adhesives, prepregs, and encapsulants; aerospace and automotive (structural) components and reinforcements.
Manufacturers & Distributors
Brand Names
1Huntsman benzoxazine brochure, "High-Performance Materials for Extreme Environments" (2015)
2Benzoxazines are sometimes used as coreactants for bismaleimides to improve their performance.