Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Properties
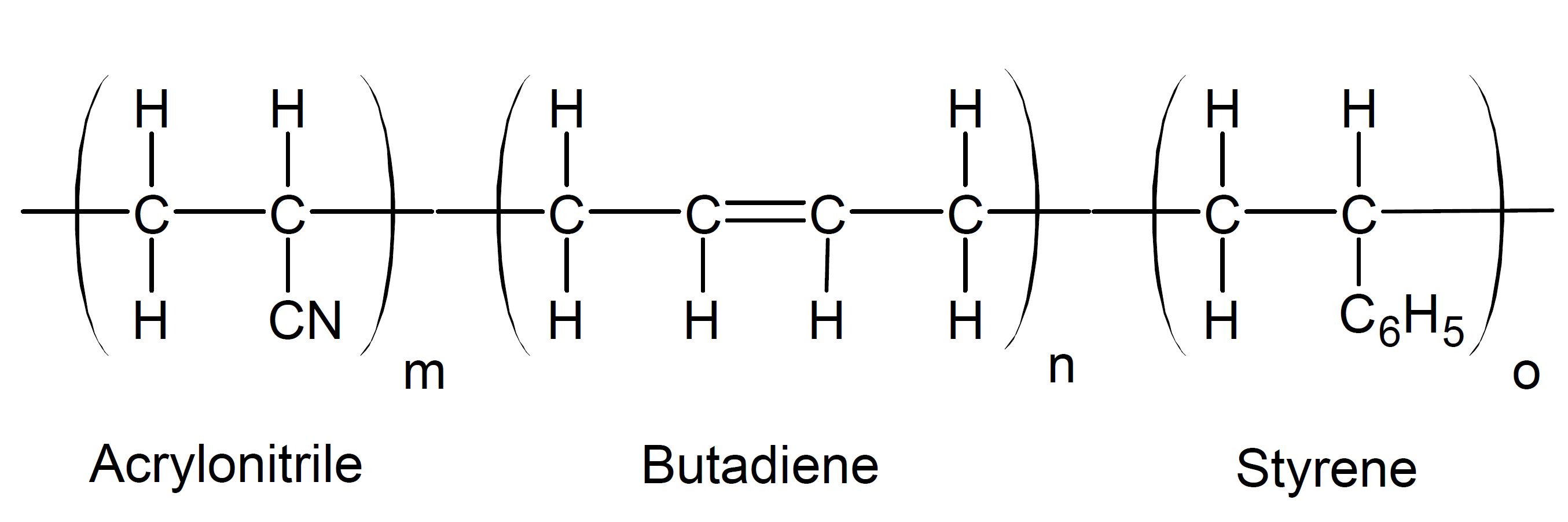
Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) is an opaque low cost thermoplastic that has high stress and impact resistance and higher tensile strength than pure polystyrene and polyacrylonitrile. The butadiene portion provides flexibility and high impact resistance whereas the styrene-acrylonitrile portion provides strength, good dimensional stability, and creep and heat resistance.1 ABS and its blends can be considered engineering thermoplastics because their properties can be tailored over a wide range for a large number of applications with a broad range of processing methods which permits the manufacture of high quality, very durable plastic products suitable for many technically demanding applications.2
Applications
ABS resins are widely used in many markets including consumer, automotive, construction, and electronics industries. Some grades are FDA compliant for use in food processing applications and thus, can be used in kitchen appliances and food processing equipment. ABS is also extensively used for toys including Lego and Kre-O bricks. Other important uses include housings for consumer electronics and small appliances, automotive consoles and panels, lamp and mirror housings, electronic plugs, wiring devices, keyboards as well as computer and printer housings.