Chloropolyethylene (CM, CPE)
Properties
Chloropolyethylene elastomers (CM, CPE) can be considered a superior type of chloroprene, having better heat and chemical resistance. They are produced by chemical substitution of hydrogen on the (linear) polyethylene backbone by chlorine atoms.
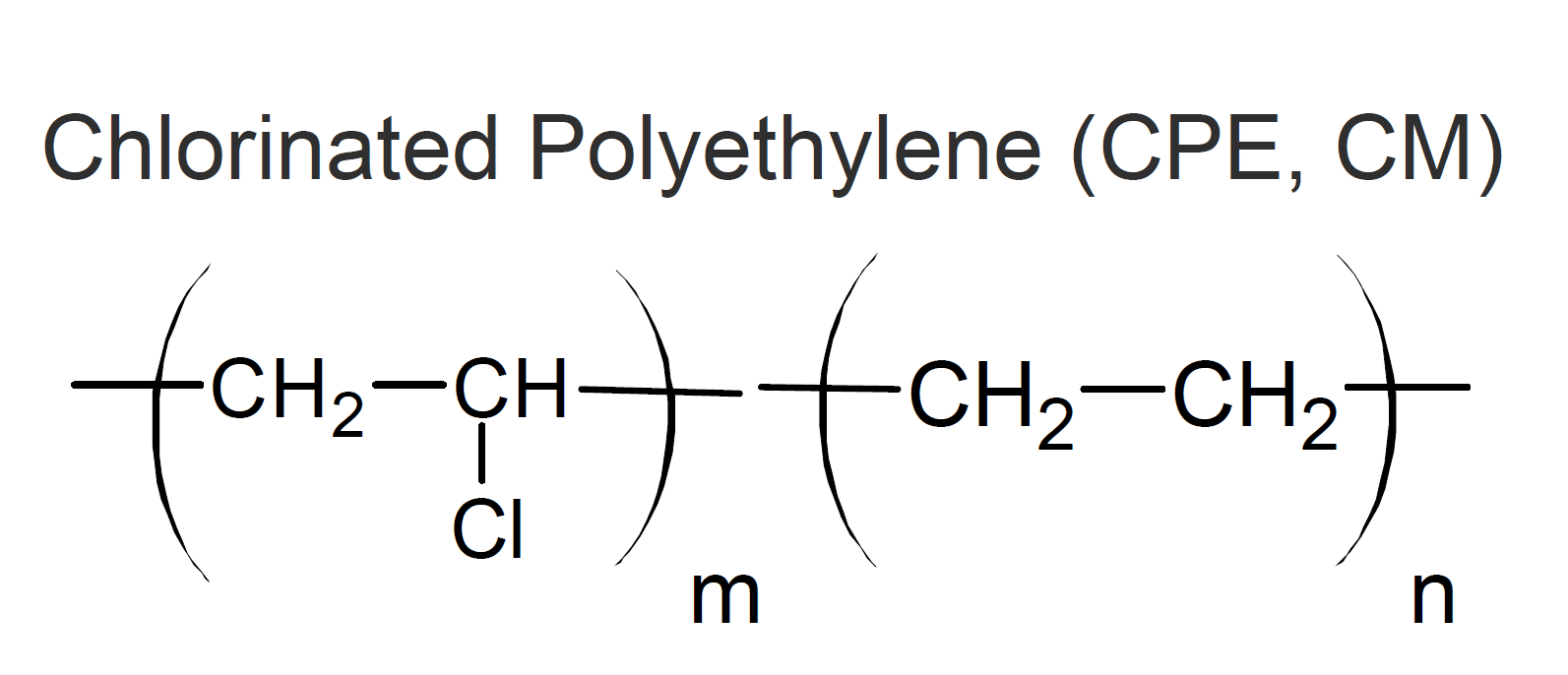
The (molded) parts are typically crosslinked with peroxyesters (BPO) or sulfur donors (Thiadiazole) using amine accelerators or by irradiation. To reduce cost and/or to improve certain properties such as flame, heat and chemical resistance, CPE resins are often compounded with fillers, plasticizers, and flame retardants prior to molding.
CPE grades usually contain 25 to 45 percent by weight chlorine which provides excellent resistance to ozone, UV, weathering, and many chemicals.1 CPEs also have good resistance to dry heat up to 150°C, low flammability, good electrical properties, high tear strength, good flex fatigue characteristics, and very good abrasion resistance. On the downside, CPEs have only fair oil and fuel resistance (depending on the chlorine content and type of oil), and poor resistance to oxygenated and chlorinated organic fluids. Furthermore, their heat resistance is lower than that of most other high performance elastomers including ACM, AEM, silcone, FVQM, FKM, and FFKM.
COMMERCIAL CPE Elastomers
An important manufacturer of chlorinated polyethylene elastomers (CPE) is Dow Chemical who sells the resin under the trademark TYRIN™.
Applications
CPE elastomers are generally used in electrical applications and as protective coatings against corrosive environments. Typical applications include flexible wire and cable insulations such as welding cables, miltary and transportation wires, and appliance cord jackets. CPEs are also used as a film and sheeting material.
The typical working temperature range is between -40°C and +150°C (-40°F - 300°F).2
Notes
The chlroine content also affects the mechanical properties. For example, a higher chlorine level increases the tensile strength and hardness whereas a lower level increases the tendency toward crystallization.
-
CPEs release hydrochloric acid when exposed to temperatures above 300°F/150°C.